Conditional Probability Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Thomas White
FREE Resource
Read more
7 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is conditional probability primarily concerned with?
The probability of an event occurring given certain information.
The likelihood of an event occurring in a vacuum.
The likelihood of an event occurring without any prior information.
The probability of two independent events occurring simultaneously.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
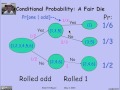
In the context of a fair die, what is the probability of rolling a one?
1/4
1/6
1/3
1/2
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does additional information affect the probability of rolling a one if an odd number is rolled?
It changes to 1/4.
It becomes 1/2.
It changes to 1/3.
It remains 1/6.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of using a probability tree?
To visualize the outcomes of a single event.
To calculate the probability of multiple events occurring in sequence.
To determine the probability of an event without any conditions.
To simplify the calculation of independent events.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the product rule in probability state?
The probability of an event is the square of its individual probability.
The probability of two events occurring is the product of their individual probabilities.
The probability of two independent events is the sum of their probabilities.
The probability of two events occurring is the product of the probability of the first event and the conditional probability of the second event given the first.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the probability of outcomes not in event A when conditioning on A?
They remain unchanged.
They are assigned a probability of 1.
They are doubled.
They are assigned a probability of 0.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What must be verified to ensure a new probability measure is valid?
The sum of the outcome probabilities must be less than 1.
The sum of the outcome probabilities must be greater than 1.
The sum of the outcome probabilities must be zero.
The sum of the outcome probabilities must equal 1.
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Figurative Language Review
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

20 questions
Graphing Inequalities on a Number Line
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

12 questions
Exponential Growth and Decay
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Exponent Rules Review
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

25 questions
Complementary and Supplementary Angles
Quiz
•
7th - 10th Grade

12 questions
Add and Subtract Polynomials
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

13 questions
Model Exponential Growth and Decay Scenarios
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Combine Like Terms and Distributive Property
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

27 questions
7.2.3 Quadrilateral Properties
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade