
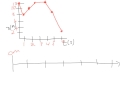
Understanding Position-Time Graphs and Motion Maps
Interactive Video
•
Physics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard

Evelyn Hayes
FREE Resource
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary focus of the video tutorial?
Exploring advanced physics concepts
Understanding the relationship between position-time graphs and motion maps
Learning about different types of graphs
Studying the history of motion maps
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the motion map example, what is the initial position of the object?
2 meters
3 meters
1 meter
0 meters
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is a stop in motion represented on a position-time graph?
A flat line
A downward slope
A steep slope
An upward slope
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a steeper slope on a position-time graph indicate?
Slower velocity
Faster velocity
Constant velocity
No movement
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
When converting a position-time graph to a motion map, what does a change in direction require?
A pause in motion
A jump in the motion map
A steep slope
A continuous line
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is a direction change without stopping shown on a motion map?
By adding a dot
By jumping underneath
By drawing a continuous line
By removing a dot
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does two dots underneath each other on a motion map indicate?
A change in direction
A stop in motion
A decrease in speed
An increase in speed
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Exit Check 4.1 - Destructive Processes
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.2 - Constructive Forces
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.3 - Conservation of Momentum
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.4 - Momentum Calculations
Quiz
•
9th Grade

21 questions
EM Spectrum
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Graphs of Motion, Velocity & Acceleration
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

21 questions
PE & KE Practice
Quiz
•
8th - 11th Grade