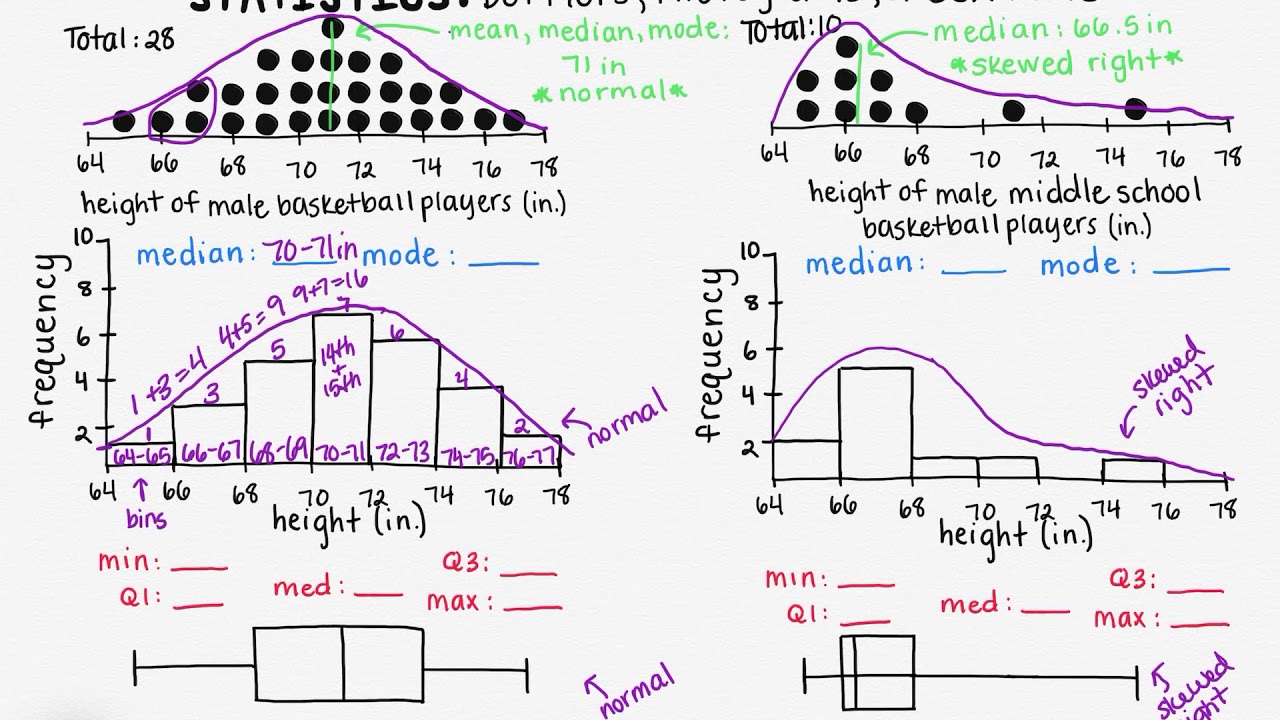
Understanding Dot Plots, Histograms, and Box Plots
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
+2
Standards-aligned

Wayground Content
FREE Resource
Enhance your content in a minute
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary advantage of using dot plots for data representation?
They are easier to create than histograms.
They provide a clear view of each data point's distribution.
They do not require knowledge of quartiles.
They can accurately calculate mean values.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.B.4
CCSS.6.SP.B.5
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What characteristic of dot plots makes them unique compared to histograms and box plots?
Ability to show exact values for each data point.
More accurate representation of skewed data.
Simpler calculation of mean values.
Easier identification of quartiles.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.A.3
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you identify a normal distribution in a histogram?
By counting the number of peaks.
By the length of the bars.
By observing a symmetrical bell-shaped curve.
By noticing a skewed distribution of data.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.A.2
CCSS.6.SP.B.4
CCSS.6.SP.B.5
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What indicates a skewed right distribution in a box plot?
All data points are on the right side.
The right side of the box is stretched out.
The median is closer to the top of the box.
The left side of the box is stretched out.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.A.2
CCSS.6.SP.B.4
CCSS.6.SP.B.5
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is a skewed right distribution identified in a histogram?
When all bars are of equal height.
When there is a tail on the right side.
When the left side has longer bars.
When the bars form a symmetrical shape.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.B.4
CCSS.HSS.ID.A.1
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why can't the mean be accurately calculated using a histogram?
Because histograms do not show individual data points.
Because histograms only display the median.
Because histograms only show the mode.
Because histograms are only used for skewed data.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.B.4
CCSS.HSS.ID.A.1
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the context of histograms, what are 'bins'?
The lines dividing the histogram into four parts.
The peaks of each bar representing the mode.
The individual data points within each range.
Ranges of values each bar represents.
Tags
CCSS.6.SP.B.4
CCSS.HSS.ID.A.1
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Identify Loci!
Quiz
•
10th Grade - University

10 questions
Revision 2
Quiz
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Geometry Midpoint and Distance Formula Quiz
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

10 questions
REFUERZO EVALUACIÓN 3 ALGEBRA
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Latihan soal KSN matematika SD
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Mental math Competition - Math Week (5-6)
Quiz
•
5th - 6th Grade

15 questions
GEOMETRICAL TERMS
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade

10 questions
6.EE.9 Independent and Dependent Variables
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

5 questions
This is not a...winter edition (Drawing game)
Quiz
•
1st - 5th Grade

15 questions
4:3 Model Multiplication of Decimals by Whole Numbers
Quiz
•
5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
The Best Christmas Pageant Ever Chapters 1 & 2
Quiz
•
4th Grade

12 questions
Unit 4 Review Day
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Identify Iconic Christmas Movie Scenes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

18 questions
Kids Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
KG - 5th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

10 questions
Identify Iconic Christmas Movie Scenes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

15 questions
Solving Equations with Variables on Both Sides Review
Quiz
•
8th Grade

15 questions
scatter plots and trend lines
Quiz
•
8th Grade

21 questions
Convert Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
Solving Systems of Equations by Graphing
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Exponents
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
One step Equations
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Christmas Movie Trivia
Quiz
•
7th Grade
