- Resource Library
- Math
- Geometry
- Midsegment Of A Triangle
- Angles Triangle Pythagoreantheor Converse Midsegments Assessment
Angles-Triangle-PythagoreanTheor-Converse-Midsegments Assessment
Authored by Antoinette Norris Woodson
Mathematics
10th Grade
CCSS covered
Used 1+ times

AI Actions
Add similar questions
Adjust reading levels
Convert to real-world scenario
Translate activity
More...
Content View
Student View
30 questions
Show all answers
1.
MATCH QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts
obtuse angle
exactly 90 degrees
right angle
exactly 180 degrees
straight angle
greater than 90 degrees, but less than 180 degrees
acute angle
less than 90 degrees
Tags
CCSS.4.G.A.1
2.
MATCH QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts

Match the following statements with their corresponding mathematical principles.
Difference of side lengths
The sum of the side lengths of the two smaller squares is equal to the side length of the large square.
Sum of side lengths
The difference of the areas of the two smaller squares is equal to the area of the large square.
Difference of areas
The differences of the side lengths of the two smaller squares is equal to the side length of the large square.
Pythagorean Theorem
The sum of the areas of the two smaller squares is equal to the area of the large square.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
3.
OPEN ENDED QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts

In an isosceles triangle ABC, m ∠ ABC = 46°, then m ∠ BAC =?
Evaluate responses using AI:
OFF
Tags
CCSS.HSG.CO.C.11
4.
CATEGORIZE QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts

A triangle has a 50-degree angle and two sides that are each 4 cm in length. Select True or False for each statement about this triangle.
Groups:
(a) True
,
(b) False
One of the angles might be 60 degrees.
Two of the angles absolutely MUST be 50 degrees.
One of the angles inside the triangle might be 65 degrees.
The triangle might be an equilateral triangle.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.A.5
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts
Which of the following statements is true about the Pythagorean theorem?
It applies to all triangles.
It only applies to isosceles triangles.
It only applies to right-angled triangles.
It applies to all quadrilaterals.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
6.
MATCH QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts
Match the following:
Corresponding Angles

Alternate Exterior Angles

Alternate Interior Angles

Same-side Interior Angles

Tags
alternate interior angles
same-side interior
alternate exterior angles
Corresponding angles
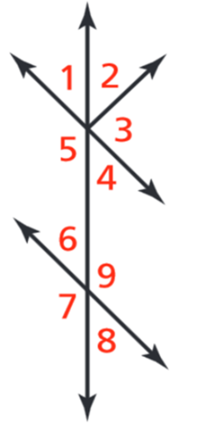
7.
MATCH QUESTION
15 mins • 5 pts

Match the following
53o
∠1
101o
∠2
79o
∠3
Answer explanation

Tags
CCSS.8.G.A.5
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

25 questions
Simple Machines
Quiz
•
KG - University

25 questions
UNIT 1 REVIEW - Points, Lines, and Planes
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Tawa College Algebra Books 1-5
Quiz
•
8th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Translations & Vocabulary Practice
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Scatter plots and trend lines
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Geometry Points, Lines & Planes
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Algebra I Regents Review #1
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Measurements and Units
Quiz
•
10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Probability Practice
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Probability on Number LIne
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

6 questions
Appropriate Chromebook Usage
Lesson
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Greek Bases tele and phon
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

23 questions
TSI Math Vocabulary
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Plotting Points on a Coordinate Plane: Quadrant 1 Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Abiotic and Biotic Factors in Ecosystems
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
SSS/SAS
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
Quiz
•
4th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Solving One Step Equations: Key Concepts and Techniques
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Special Right Triangles
Quiz
•
10th Grade

16 questions
Circle Vocabulary
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade