
AP Physics Kinematic Equations and Freefall
Authored by Charles Martinez
Physics
9th - 12th Grade
NGSS covered
Used 4+ times

AI Actions
Add similar questions
Adjust reading levels
Convert to real-world scenario
Translate activity
More...
Content View
Student View
15 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
3 mins • 1 pt
Juan is standing on the top observation deck of the Eiffel Tower in Paris at a height of 300 meters. He drops his cell phone. How fast will the phone be traveling when it hits the ground? Ignore the effect of air resistance.
9.8 m/s
76.68 m/s
149.76 m/s
46.99 m/s
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-4
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
If an object is in free fall for three seconds, how fast will it be falling?
9.8 m/s
19.6 m/s
29.4 m/s
39.2 m/s
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
NGSS.HS-PS2-4
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

What happens to the velocity of a ball as it is dropped off a cliff?
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

What does this graph represent?
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
A man drops his camera off of the top of the oil derrick tower at Six Flags. Which of the following kinematic equations would he use in order to calculate the speed the camera was travelling when it hit the ground?
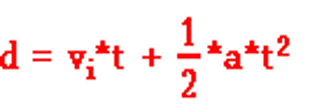
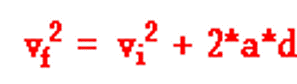
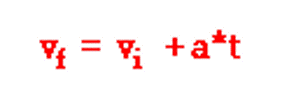
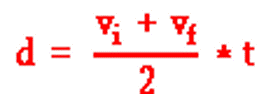
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Alexis is riding her bike around town. She travels 43.2 m to the right, and then turns around to bike an additional 30 m to the left. Determine the velocity of Alexis's bike ride if it takes her 39.4 seconds to complete her motion.
2 m/s to the right
2 m/s to the left
0.3 m/s to the right
0.3 m/s to the left
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a constant velocity do tour our acceleration?
Acceleration increases
Acceleration decreases
Acceleration is zero
Acceleration is not affected by velocity
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

19 questions
Standing Waves
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Physics
Quiz
•
8th Grade - Professio...

15 questions
PHYSICS 1 - 2ND QUARTER CONCEPT REVIEWER
Quiz
•
12th Grade

15 questions
Campo eléctrico, ley de Coulomb y potencial eléctrico
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

20 questions
FREE FALL
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
PAS FISIKA KELAS XI MIA
Quiz
•
11th Grade

18 questions
Listrik Bolak-balik
Quiz
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Thin Lens Equation Sign Conventions
Quiz
•
10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Exit Check 3.1 - Kepler's Laws
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.2 - Force of Gavity
Quiz
•
9th Grade

21 questions
Potential and Kinetic Energy
Quiz
•
11th Grade

27 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Circuits Review Quiz
Quiz
•
12th Grade

20 questions
Unit 8 - Energy Test - 2025-2026
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

19 questions
Generators, Motors, and Transformers
Quiz
•
8th Grade - University

13 questions
Series Circuits and Parallel Circuits
Quiz
•
12th Grade