
Slow and Rapid Changes
Quiz
•
Science
•
5th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
+2
Standards-aligned

Map Munoz
Used 430+ times
FREE Resource
Enhance your content in a minute
20 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
5 mins • 1 pt

The Rio Grande Valley is located at the southern tip of Texas at the end of a long river known as the Rio Grande. How did the delta at the end of the Rio Grande form? (5.7B)
Sand and mud from the Gulf of Mexico were washed ashore by tsunamis.
The river cut through the solid bedrock of the valley.
The river deposited large amounts of sediment from land erosion.
Hurricanes pushed soil and debris from the Gulf of Mexico onto the land.
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
5 mins • 1 pt

The photograph shows a canyon in northern Arizona. Which of these describes how this canyon was most likely formed? (5.7B)
Floods eroded the sandstone away from the canyon walls.
Glaciers eroded the canyon rock as they melted and moved.
Ice wedged into cracks in the rock and weathered the canyon walls.
Wind blew large rocks that smashed against the canyon walls.
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
5 mins • 1 pt

A wide U-shaped valley is shown in the photograph. This valley was most likely formed by-- (5.7B)
flash flooding
a glacier
a hurricane
melting snow
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
5 mins • 1 pt
The Grand Canyon is more than 400 km long and in some places almost 2 km deep. Which model best represents the main process that formed the Grand Canyon? (5.7B)
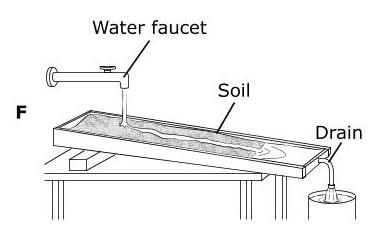
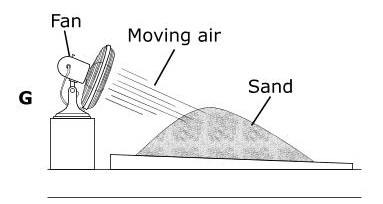
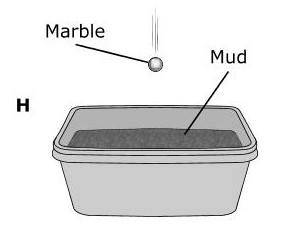
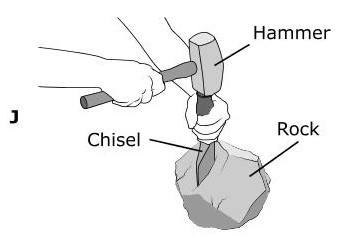
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
5 mins • 1 pt

A scientist was studying a type of event that occurred on Earth in various places within a 30-day period. The circles indicate where the events happened. The events being studied involved rapid changes to Earth's surface at the locations shown on the map. What type of event do the circles on the map most likely represent? (3.7B)
Landslides, because they are all located along ocean coastlines
Volcanoes, because they occur only near the equator
Earthquakes, because they occur on land and on the ocean floor
Floods, because heavy rains can make riverbeds deeper and create deltas
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt

When earth materials have been eroded and are put (dropped) into a new location is called.
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt

The breaking down of rock materials on the surface of the earth is called?
Tags
NGSS.MS-ESS2-2
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

19 questions
Ricks and Minerals
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Land Formation
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Matter and Their Properties
Quiz
•
5th Grade - University

15 questions
Phases of the Moon II
Quiz
•
5th Grade

17 questions
Planets Notes
Quiz
•
4th - 5th Grade

20 questions
Food Groups
Quiz
•
4th - 7th Grade

18 questions
Robot Characteristics Quiz
Quiz
•
5th Grade

18 questions
MIXTURE QUIZ 2
Quiz
•
5th - 6th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

20 questions
The Water Cycle
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition
Quiz
•
5th Grade

28 questions
4th Grade The Need for Speed
Quiz
•
3rd - 5th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs Review
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
The Water Cycle
Quiz
•
4th - 5th Grade

21 questions
Solar System Review
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Food Webs
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Earth Processes and Landforms
Quiz
•
5th Grade



