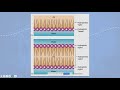
Exploring Membrane Permeability: The Case of Water
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Medium
Jackson Turner
Used 1+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is it important to memorize what can or cannot pass through a cell membrane?
To know the history of cell biology
To understand cell structure
For upcoming tests and worksheets
To learn about cell division
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following gases can pass through the cell membrane via simple diffusion?
Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates
Water, Ethanol, Benzene
Glucose, Calcium, Sodium
Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, Nitrogen
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of molecules require a protein channel or pump to pass through the cell membrane?
Basic gases
Hydrophobic molecules
Large polar molecules
Small polar molecules
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why do polar materials struggle to pass through the hydrophobic lipid tails?
Because they are charged
Because the lipid tails avoid water
Because they are non-polar
Because they are too large
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when phospholipids are placed in water?
They become hydrophilic
They point their tails towards each other
They form a single layer
They dissolve completely
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can water, despite being polar, pass through the hydrophobic region of the cell membrane?
Because it is large
Because it is charged
Because it is non-polar
Because it is small
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What factors can help water pass through the hydrophobic region more easily?
Decreased membrane fluidity
Decreased pressure
Increased pressure and membrane fluidity
Increased temperature
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Exploring the Cell Membrane
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Passive Transport Mechanisms in Cells
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Homeostasis and Transport Concepts Explained
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Membrane Transport: Passive vs. Active Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Structure and Function Concepts
Interactive video
•
7th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Plasma Membrane Structure and Functions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Cell Membrane Structure and Function
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

55 questions
CHS Student Handbook 25-26
Quiz
•
9th Grade

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Chaffey
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
PRIDE
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
6-8 Digital Citizenship Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

18 questions
Characteristics of Living Things
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

12 questions
Macromolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

23 questions
Lab Equiptment/ Lab Safety
Quiz
•
7th Grade

19 questions
H Energy Transfer Vocabulary
Quiz
•
9th Grade

11 questions
Enzymes
Lesson
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Biomolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

27 questions
Flinn - Lab Safety Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade