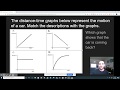
Exploring Distance-Time Graphs
Interactive Video
•
Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Standards-aligned
Sophia Harris
FREE Resource
Standards-aligned
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main difference between speed and velocity?
Velocity is measured in meters, speed in seconds.
Speed includes direction, velocity does not.
Velocity includes direction, speed does not.
Speed is always constant, velocity changes.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a distance-time graph, what does a horizontal line indicate?
Constant speed
Acceleration
Deceleration
No motion
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a straight line in a distance-time graph represent?
No motion
Constant speed
Acceleration
Changing speed
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you identify acceleration in a distance-time graph?
By a horizontal line
By a straight line
By a curved line
By a downward slope
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a curved line in a distance-time graph indicate?
Constant speed
No motion
Acceleration
Deceleration
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of motion is represented by a straight line that changes slope in a distance-time graph?
Variable speed
Constant speed
Acceleration
Deceleration
Tags
NGSS.MS-PS3-1
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a distance-time graph, what does a line that goes up and then becomes horizontal indicate?
Deceleration followed by rest
Acceleration followed by constant speed
Constant speed followed by rest
Constant speed followed by acceleration
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

11 questions
Valentines Day
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles and Functions
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
Quiz
•
6th Grade

8 questions
Newton's Second Law
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Thermal Energy - Heat Transfer
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Rock Cycle: Types and Formation
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Carbon Cycle
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade