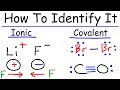
Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Explained
Interactive Video
•
Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
+1
Standards-aligned
Sophia Harris
Used 6+ times
FREE Resource
Standards-aligned
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of bond is typically formed between a metal and a non-metal?
Ionic bond
Covalent bond
Metallic bond
Hydrogen bond
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is true about covalent bonds?
They involve the transfer of electrons.
They always result in the formation of ions.
They are usually formed between a metal and a non-metal.
They involve the sharing of electrons.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the molecule Br2, what type of bond is present?
Polar covalent bond
Nonpolar covalent bond
Ionic bond
Metallic bond
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS1-1
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the electronegativity difference range for a nonpolar covalent bond?
0.1 or less
1.0 or more
0.5 or more
0.4 or less
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which bond is considered nonpolar in the molecule CH4?
H-H bond
C-O bond
C-H bond
C-C bond
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of bond is present between carbon and oxygen in CO?
Polar covalent bond
Metallic bond
Nonpolar covalent bond
Ionic bond
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to lithium when it loses an electron in the formation of lithium fluoride?
It forms a covalent bond.
It remains neutral.
It becomes positively charged.
It becomes negatively charged.
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS1-1
NGSS.HS-PS1-2
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

20 questions
Cell Organelles and Functions
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

33 questions
Grade 6 Quarter 3 PMA 5 Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
Quiz
•
6th Grade

12 questions
Ecological Succession
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Thermal Energy - Heat Transfer
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Rock Cycle: Types and Formation
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Layers of the Earth
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

15 questions
Punnett Squares
Quiz
•
6th Grade