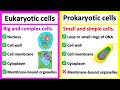
Differences Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Easy
Mia Campbell
Used 1+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
6 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main focus of this video?
The structure of animal cells
The difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
The process of photosynthesis
The lifecycle of bacteria
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is a characteristic of eukaryotic cells?
They have membrane-bound organelles
Their genetic material is free-floating
They are always unicellular
They lack a nucleus
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following organisms are examples of eukaryotes?
Fungi only
Animals and plants
Viruses
Bacteria
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a defining feature of prokaryotic cells?
Their genetic material is not enclosed in a nucleus
They are multicellular
They have membrane-bound organelles
They have a nucleus
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In what form is the genetic material found in prokaryotic cells?
In chromosomes
In a loop or small rings of DNA
In the nucleus
In mitochondria
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is an example of a prokaryote?
Bacteria
Animals
Plants
Fungi
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Exploring the Functions of Cell Organelles
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Nucleus and Its Functions
Interactive video
•
7th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring the Distinctions Between Viruses and Bacteria
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Types and Their Differences
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Cells - Components of the Nucleus
Interactive video
•
6th - 9th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Cell Biology Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Cell Organelles in Biology
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Cell Theory and Organelles
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Appointment Passes Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Grammar Review
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

23 questions
Lab Equiptment/ Lab Safety
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Scientific method
Interactive video
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Section 3 - Macromolecules and Enzymes
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade