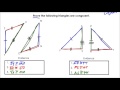
Exploring SSS and SAS Congruence in Triangles
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
+2
Standards-aligned
Amelia Wright
FREE Resource
Standards-aligned
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does it mean for two triangles to be congruent?
Only one pair of corresponding sides is equal.
All corresponding sides are equal but angles are different.
All corresponding angles are equal but sides are different.
All corresponding angles and sides are equal.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.A.2
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is a shortcut to prove triangle congruence?
Side-Angle-Angle
Angle-Side-Angle
Side-Side-Side
Angle-Angle-Angle
Tags
CCSS.HSG.SRT.B.5
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
If two triangles have three pairs of congruent sides, what can be concluded?
The triangles are isosceles.
The triangles are congruent.
The triangles are similar.
The triangles are right-angled.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.A.2
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the given example, why are the triangles not congruent?
Because no sides are congruent.
Because only two sides are congruent.
Because all sides are congruent.
Because only one side is congruent.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.A.2
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the second shortcut to prove triangle congruence introduced in the lesson?
Angle-Angle-Side
Side-Angle-Side
Angle-Side-Angle
Side-Side-Angle
Tags
CCSS.HSG.SRT.B.5
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
For SAS congruence, where must the angle be located?
Between the two congruent sides.
At the top of the triangle.
At the vertex of the triangle.
At the base of the triangle.
Tags
CCSS.HSG.SRT.B.5
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why can't the triangles be proven congruent using SAS in the given example?
The sides are not congruent.
The angles are not congruent.
The angle is not between the two sides.
The triangles are not similar.
Tags
CCSS.HSG.SRT.B.5
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Finding Missing Angles and Sides in Congruent Figures
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Mastering CPCTC in Triangle Congruence Proofs
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Constructing Parallel Lines and Triangles
Interactive video
•
7th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Right Triangle Congruence Theorems Explained
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Congruent Triangle Rules
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Triangle Congruence: SSS & SAS Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Congruent Triangles and Angles
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Appointment Passes Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Grammar Review
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
Perfect Squares and Square Roots
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Integers, Integers, Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Adding and Subtracting integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Adding and Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
6th - 7th Grade

21 questions
Convert Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
Quiz
•
6th Grade

17 questions
Classifying Real Numbers
Quiz
•
8th Grade