Muscle Contraction Mechanisms
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Lucas Foster
FREE Resource
Read more
5 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
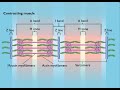
What is the arrangement of actin and myosin myofilaments in a relaxed muscle?
They are completely separated.
They lie side by side.
They are intertwined.
They form a spiral structure.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the actin myofilaments during muscle contraction?
They are pulled toward the center of the myosin.
They dissolve.
They remain stationary.
They are pushed away from the myosin.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the result of the interaction between actin and myosin myofilaments during contraction?
The muscle becomes rigid.
The sarcomeres shorten.
The myofilaments break apart.
The muscle elongates.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a fully contracted muscle, what happens to the H zones?
They expand.
They disappear.
They double in size.
They become more prominent.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What change occurs to the I band in a fully contracted muscle?
It disappears completely.
It becomes wider.
It remains unchanged.
It becomes very narrow.
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Muscle Physiology and Function Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms and Proteins
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Motor Proteins: Tiny Pirates in Your Cells
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Neuromuscular Junction and Muscle Contraction
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

2 questions
Anatomy and Physiology BTEC Sport Level 3 Unit 1- Types of Muscles
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Exploring the Muscular System: Anatomy and Function
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Cell Structure and the Cytoskeleton
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Membrane and Transport
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Section 3 - Macromolecules and Enzymes
Quiz
•
10th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade