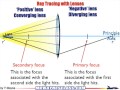
Ray Tracing and Lens Properties
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Lucas Foster
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a key characteristic of a converging lens?
Thicker at the edges
Thinner in the middle
Flat on both sides
Thicker in the middle
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the thin lens approximation, where does the light bend?
At the edge of the lens
At the focal point
At the line of refraction
At the surface of the lens
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary focus in a spherical lens approximation?
Half the radius of the circle
Twice the radius of the circle
The center of the lens
The edge of the lens
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when the light source is moved to the other side of the lens?
The primary and secondary sides switch
The lens becomes thicker
The lens becomes a diverging lens
The focal length changes
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which ray is drawn parallel to the principal axis in ray tracing?
The first ray
The virtual ray
The second ray
The third ray
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the easiest ray to draw in ray tracing?
The virtual ray
The ray through the vertex
The ray through the secondary focus
The ray through the primary focus
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the third ray in ray tracing different from the first?
It goes through the secondary focus first
It goes through the primary focus first
It is refracted at the vertex
It is not refracted
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Lens Properties and Image Formation
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Understanding Convex and Concave Lenses
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Understanding Two-Lens Systems
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Camera Basics - Aperture
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
The Microscope: Parts of the Compound Microscope
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Convex Lenses: Refraction and Image Formation
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Amscope Microscope Functionality and Features
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Lens Properties and Image Formation
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

40 questions
LSHS Student Handbook Review: Pages 7-9
Quiz
•
11th Grade

24 questions
Scientific method and variables review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Mental Health Vocabulary Pre-test
Quiz
•
9th Grade