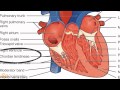
Heart Anatomy and Function Assessment
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Lucas Foster
Used 4+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the function of the tricuspid valve in the heart?
To separate the left and right ventricles
To pump blood into the aorta
To prevent backflow of blood into the right atrium
To oxygenate the blood
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which arteries are unique for carrying deoxygenated blood?
Aortic arteries
Pulmonary arteries
Carotid arteries
Coronary arteries
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the mitral valve in the heart?
To pump blood into the pulmonary trunk
To allow blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle
To prevent blood from entering the vena cavae
To separate the atria from the ventricles
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the outermost layer of the heart called?
Visceral pericardium
Parietal pericardium
Myocardium
Endocardium
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the function of the chordae tendinae?
To oxygenate the blood
To separate the atria from the ventricles
To attach valves to the papillary muscles
To pump blood into the ventricles
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the fossa ovalis a remnant of?
The interventricular septum
The foramen ovale
The coronary sinus
The ligamentum arteriosum
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the papillary muscles?
To separate the ventricles
To pump blood into the atria
To oxygenate the blood
To contract and prevent backflow into the atria
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Circulatory System Functions and Structures
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring the Circulatory System: Functions and Circuits
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Cardiovascular System (An Introduction)
Interactive video
•
6th - 9th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Heart Functions and Blood Circulation
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Circulatory System Concepts and Functions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Human Circulatory and Respiratory System
Interactive video
•
7th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Blood Vessels and Circulation Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Heart Anatomy and Function Assessment
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade