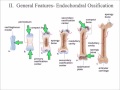
Bone Growth and Ossification Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
Aiden Montgomery
Used 19+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of osteoblasts in bone formation?
To maintain bone
To destroy bone
To build bone
To convert cartilage to bone
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of ossification is responsible for the formation of flat bones?
Epiphyseal ossification
Periosteal ossification
Endochondral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does 'endo' refer to in endochondral ossification?
Inside
Above
Between
Outside
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Where is the primary ossification center located in a long bone?
In the epiphysis
In the diaphysis
In the medullary cavity
In the periosteum
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What role do chondrocytes play in endochondral ossification?
They make cartilage
They convert bone to cartilage
They maintain bone
They destroy bone
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the function of the epiphyseal plate during bone growth?
To convert bone to cartilage
To maintain bone density
To stop bone growth
To allow bone lengthening
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when there is no more cartilage between the epiphysis and diaphysis?
Bone becomes cartilage
Bone growth continues
Bone growth stops
Bone density decreases
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Did Cod Save the Vikings?
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

8 questions
CLEAN : Top ballet students back training for increasingly 'fragile' career
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Anatomy and Physiology: Breathing and Respiratory System
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Paleontology Discoveries and Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
eDNA and Cardiac Fibroblasts Insights
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Biceps and Triceps Anatomy Questions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Vocal Anatomy and Function Assessment
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Anatomy of the Nasal and Oral Cavities
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

5 questions
This is not a...winter edition (Drawing game)
Quiz
•
1st - 5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Identify Iconic Christmas Movie Scenes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

18 questions
Kids Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
KG - 5th Grade

11 questions
How well do you know your Christmas Characters?
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
How the Grinch Stole Christmas
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Stages of Meiosis
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 2 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
DNA & Protein Synthesis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
AP Biology: Unit 3 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

30 questions
VCS Biology_ Unit 5_DNA Structure/Function & Replication
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

82 questions
Fall Semester Exam Review 2025
Quiz
•
9th Grade