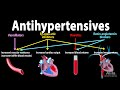
Hypertension Treatment and Mechanisms
Interactive Video
•
Science, Biology, Health
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Medium
Aiden Montgomery
Used 2+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the most common cause of hypertension?
Increased cardiac output
Narrower or stiffer blood vessels
Large blood volume
Excess venous return
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which class of diuretics is most commonly prescribed for hypertension?
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Loop diuretics
Thiazides
Potassium-sparing diuretics
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of diuretic is often used in combination with others to prevent potassium loss?
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Potassium-sparing diuretics
Thiazides
Loop diuretics
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a potential side effect of alpha-1-blockers?
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Sedation
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of medication is typically used as a first-line treatment for hypertension?
Beta-blockers
Alpha-blockers
Central sympatholytics
Non-selective adrenergic antagonists
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary action of ACE inhibitors?
Stimulate alpha-2 receptors
Inhibit L-type calcium channels
Increase cardiac output
Block conversion of angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a type of vasodilator?
Beta-blockers
Nitrodilators
Direct arterial vasodilators
Calcium channel blockers
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Diuretics and Their Effects
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Runners warm up on race start line
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Respiratory Alkalosis Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Hypovolemic Shock Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
What Happens When a Venomous Snake Bites Itself?
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Understanding Acute Coronary Syndrome and Related Concepts
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS)
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Enzyme Inhibition Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

11 questions
NEASC Extended Advisory
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

10 questions
Boomer ⚡ Zoomer - Holiday Movies
Quiz
•
KG - University

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Multiplying and Dividing Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

10 questions
Exploring Newton's Laws of Motion
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the States of Matter
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

16 questions
Macromolecules Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Biomes and Ecosystems for Kids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Laws in NFL Action
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

15 questions
Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factors
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Thermal Energy and Temperature Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade