
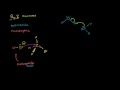
Understanding Sn2 Reactions
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Amelia Wright
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the '2' in Sn2 reactions signify?
The rate-determining step involves two reactants.
The reaction produces two products.
The reaction involves two steps.
The reaction requires two catalysts.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In an Sn2 reaction, what role does the nucleophile play?
It accepts an electron.
It donates an electron.
It forms a double bond.
It donates a proton.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is considered a leaving group in Sn2 reactions?
Hydroxide
Hydrogen
Carbon
Bromine
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the nucleophile during the Sn2 reaction mechanism?
It is expelled from the reaction.
It becomes positively charged.
It forms a temporary bond with the substrate.
It remains unchanged.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the charge on the bromine atom after it leaves in an Sn2 reaction?
Double negative
Neutral
Negative
Positive
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following best describes a nucleophile?
A molecule that donates protons
A molecule that donates electrons
A molecule that accepts electrons
A molecule that forms covalent bonds
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the substrate in an Sn2 reaction?
It donates electrons.
It is replaced by the nucleophile.
It acts as a catalyst.
It forms a double bond.
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

22 questions
Unit 9 Gas Law Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Types of Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acids and Bases
Quiz
•
10th Grade

7 questions
GCSE Chemistry - Balancing Chemical Equations #4
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
Quiz
•
10th Grade

40 questions
Unit 3 (Part 1) Chemical Equations & Reactions Review Game
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade