
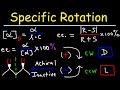
Optical Activity and Chiral Molecules
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Mia Campbell
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the term used to describe a molecule that can rotate plane-polarized light?
Optically active
Symmetrical
Optically inactive
Achiral
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is true about enantiomers?
They have different solubilities.
They have identical optical properties.
They have different boiling points.
They are mirror images of each other.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the R/S configuration of a chiral center indicate?
The physical properties of the molecule
The direction of light rotation
The solubility of the molecule
The configuration at the chiral center
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to plane-polarized light when it passes through an achiral molecule?
It remains unchanged.
It rotates to the right.
It rotates to the left.
It is absorbed completely.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is specific rotation calculated?
By dividing the observed rotation by the path length and concentration
By multiplying the observed rotation by the path length
By adding the observed rotation to the path length
By dividing the observed rotation by the concentration
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the relationship between enantiomeric excess and optical purity?
Optical purity is twice the enantiomeric excess.
They are unrelated.
Enantiomeric excess is the square of optical purity.
They are equivalent in decimal form.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a factor in determining specific rotation?
Temperature
Observed rotation
Path length
Concentration
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
La rotación y revolución de la tierra: la tierra girando
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Critique of James Tour's Arguments
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Curl of a Vector Field
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Vector Fields and Fluid Flow
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Mineral Identification and Properties
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Rotational Motion Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
The Solar System is Beige
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
EARLY CONCEPT BRAIN RESEARCH: NEXT-GENERATION OPTOGENETICS
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

22 questions
Unit 9 Gas Law Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Types of Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acids and Bases
Quiz
•
10th Grade

7 questions
GCSE Chemistry - Balancing Chemical Equations #4
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
Quiz
•
10th Grade

40 questions
Unit 3 (Part 1) Chemical Equations & Reactions Review Game
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade