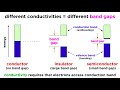
Conductivity and Semiconductors Explained Through Engaging Scenarios
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Chemistry, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary characteristic of a conductor?
It allows the flow of electrical current.
It is always made of metal.
It has a large band gap.
It does not conduct electricity.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when two atomic orbitals combine?
They create a lower-energy bonding orbital and a higher-energy antibonding orbital.
They always form a conductor.
They form a single molecular orbital.
They result in a large band gap.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the key feature of a conductor that allows it to conduct electricity?
Infinitesimally small energy difference between the highest occupied and lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals.
Electrons are tightly bound.
A large band gap.
It is made of non-metallic elements.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a band gap?
A gap in the molecular orbitals.
A gap in the atomic structure.
A physical gap in the material.
A gap in energy between the valence band and conduction band.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why do semiconductors conduct electricity better at higher temperatures?
They have a larger band gap at higher temperatures.
More thermal energy is available to promote electrons into the conduction band.
They become insulators at higher temperatures.
Their atomic structure changes at higher temperatures.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is a common semiconductor material?
Silicon
Aluminum nitride
Diamond
Copper
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the effect of doping on a semiconductor?
It turns the semiconductor into an insulator.
It increases the conductivity by introducing impurities.
It increases the band gap.
It decreases the band gap.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
How Transistors Work - A Quick and Basic Explanation
Interactive video
•
KG - University

11 questions
Understanding Transistors and Semiconductors
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Semiconductor Concepts and Properties
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
¿Cómo funciona el TRANSISTOR?
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Silicon and Its Applications
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
सेमिकंडक्टर पर आधारित क्विज़
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Diodes and Semiconductor Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Conductivity and Semiconductors
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

40 questions
LSHS Student Handbook Review: Pages 7-9
Quiz
•
11th Grade

24 questions
Scientific method and variables review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Mental Health Vocabulary Pre-test
Quiz
•
9th Grade