
Mastering Serial Dilution Techniques in Microbiology
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary purpose of serial dilution in microbiology?
To increase the concentration of bacteria in a sample
To isolate a single type of bacteria from a mixture
To dilute a sample to a manageable number of colonies
To sterilize a sample completely
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is it important to use sterile water and broth when preparing a soil sample for dilution?
To make the solution more acidic
To ensure the broth is nutrient-rich
To increase the growth rate of bacteria
To prevent contamination from external bacteria
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
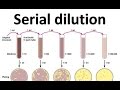
In the serial dilution process, what is the initial concentration when 1 gram of soil is mixed with 9 ml of broth?
10 to the power minus 4
10 to the power minus 2
10 to the power minus 1
10 to the power minus 3
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main reason for using the pour plate method in serial dilution?
To obtain isolated colonies from a mixed culture
To ensure even distribution of bacteria
To reduce the time required for culturing
To increase the number of colonies
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which dilution levels are typically used for obtaining a desirable number of colonies?
10 to the power minus 1 and 10 to the power minus 2
10 to the power minus 3 to 10 to the power minus 5
10 to the power minus 6 and 10 to the power minus 7
10 to the power minus 8 and 10 to the power minus 9
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the benefit of obtaining isolated colonies in microbiology?
To increase the diversity of bacteria
To make it easier to identify and study specific bacteria
To reduce the number of bacteria in a sample
To enhance the growth rate of bacteria
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can the total number of microorganisms in the original sample be calculated?
By counting the number of colonies directly
By multiplying the plate count by the dilution factor
By measuring the weight of the soil sample
By using a microscope to count individual bacteria
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

18 questions
Mendelian Genetics
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Cell Cycle and mitosis
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Plant structures and tropisms
Quiz
•
9th Grade

55 questions
Category2 SPRING 2026 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

100 questions
*NEW Biology Benchmark 1 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th Grade

72 questions
#Category 4 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade