Double Replacement Reactions and Solubility
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science, Biology
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the driving force behind a double replacement reaction?
Emission of light
Formation of a gas
Formation of a precipitate
Absorption of heat
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you determine if a compound is soluble or insoluble?
By checking its color
By using a solubility table
By measuring its temperature
By observing its smell
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a precipitate?
An insoluble product
A gaseous product
A liquid product
A soluble product
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is soluble: sodium carbonate or potassium nitrate?
Potassium nitrate
Both are soluble
Both are insoluble
Sodium carbonate
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the rule for the solubility of nitrates?
Nitrates are soluble with exceptions
Nitrates are soluble only in water
Nitrates are always soluble
Nitrates are insoluble
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a double replacement reaction, what must be formed for the reaction to occur?
A solid
A precipitate
A gas
A liquid
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
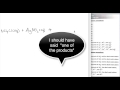
What happens if both products in a double replacement reaction are aqueous?
A gas is released
No reaction occurs
A precipitate forms
A reaction occurs
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Chemical Reactions and Equations
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Net Ionic Equations and Spectator Ions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Nickel(II) Chloride and Water Chemistry
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Net Ionic Equations and Spectator Ions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Double Replacement Reactions and Solubility
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Solubility of Ionic Compounds in Water
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Chemical Reactions Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Chemical Reactions and Products
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
9/11 Experience and Reflections
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

9 questions
Tips & Tricks
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

21 questions
Lab Safety
Quiz
•
10th Grade

12 questions
elements, compounds, and mixtures
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Significant figures and Measurements
Quiz
•
10th Grade

30 questions
Aca Nuclear Chemistry
Quiz
•
10th Grade

16 questions
Counting Sig Figs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

17 questions
CHemistry Unit 7 Dimensional Analysis Practice
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

30 questions
Unit 1.2 Nuclear Chemistry
Quiz
•
10th Grade