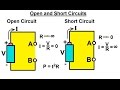
Understanding Open and Short Circuits
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Mathematics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main characteristic of an open circuit?
It allows current to flow freely.
It is always connected to a battery.
It has infinite resistance.
It has zero resistance.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the current in an open circuit according to Ohm's law?
It becomes infinite.
It remains constant.
It doubles.
It becomes zero.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a short circuit, what is the resistance between the terminals?
Very high
Moderate
Zero or nearly zero
Infinite
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a potential consequence of a short circuit near a power plant?
No current flow.
Moderate current flow.
Infinite current flow.
Limited current flow.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why can short circuits be problematic on circuit boards?
They increase the resistance.
They can cause excessive current and damage components.
They prevent any current from flowing.
They reduce the voltage.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What can excessive current in a short circuit cause in a small device?
Improved performance.
Component damage due to heat.
Increased efficiency.
Reduced power consumption.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of a circuit breaker in a household circuit?
To decrease the resistance.
To increase the voltage.
To allow more current to flow.
To stop excessive current and prevent hazards.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Voltage Drop and Circuit Behavior
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Effects of Resistance in Circuits
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Equivalent Resistance in Circuit Analysis
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Total Resistance in Circuits
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
GCSE Physics - Series Circuits #17
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Resistance in Series
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Circuit Resistance and Variables
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Total Resistance in Parallel Circuits
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

24 questions
Scientific method and variables review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Mental Health Vocabulary Pre-test
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Points, Lines, Planes
Quiz
•
9th Grade