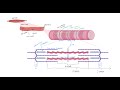
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms and Proteins
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Physical Ed
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of a sarcomere in muscle contraction?
To provide nutrients
To contract and shorten the muscle
To store energy
To protect the muscle
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the sarcolemma in muscle fibers?
It stores calcium ions
It holds myofibrils together
It generates electrical impulses
It provides structural support to bones
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which protein primarily composes the thick filament in myofibrils?
Actin
Troponin
Tropomyosin
Myosin
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the function of the Z disc in a sarcomere?
It stores ATP
It marks the boundary of a sarcomere
It binds calcium ions
It generates electrical signals
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which protein is responsible for the elasticity in muscle fibers?
Titan
Actin
Troponin
Myosin
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary role of the actin binding site on myosin?
To store energy
To bind ATP
To attach to actin
To release calcium
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What structural feature of actin allows it to form a helical structure?
Its interaction with myosin
Its single-stranded nature
Its double-stranded nature
Its ability to bind calcium
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Muscle Contraction
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Mechanics: The Romance of Actin and Myosin
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Sliding Filament Model
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Skeletal Muscle Function
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

7 questions
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms and Structures
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Tissue Structure and Function in the Human Body
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

55 questions
CHS Student Handbook 25-26
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Afterschool Activities & Sports
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
PRIDE
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
Cool Tool:Chromebook
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Bullying
Quiz
•
7th Grade

18 questions
7SS - 30a - Budgeting
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

12 questions
Macromolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

11 questions
Enzymes
Lesson
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Biomolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

27 questions
Flinn - Lab Safety Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
10th Grade