
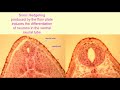
Sonic Hedgehog and Neural Development
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Other
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
9 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial source of Sonic Hedgehog in the nervous system?
The brain
The notochord
The spinal cord
The neural crest
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the neural tube is primarily affected by Sonic Hedgehog for differentiation?
Lateral plate
Floor plate
Basal plate
Roof plate
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does Sonic Hedgehog help cells determine their position in the ventral nerve tube?
By altering their shape
Through a concentration gradient
Through electrical signals
By changing their color
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of neurons are formed in the ventral portion of the neural tube due to Sonic Hedgehog?
Oligodendrocytes
Glial cells
Motor neurons
Sensory neurons
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a type of inter neuron mentioned in the transcript?
V0 inter neurons
V1 inter neurons
V2 inter neurons
V3 inter neurons
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of motor neurons formed in the ventral neural tube?
To regulate hormone levels
To process visual information
To send axons to muscles and glands
To send sensory information to the brain
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of commissural fibers in the nervous system?
They stay on the same side of the spinal cord
They connect the brain to the spinal cord
They connect muscles to nerves
They cross to the opposite side of the spinal cord or brain
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Muscle Contraction Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Nervous System
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
12.3 Electrical Signals in Neurons (16min)
Interactive video
•
11th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Community gardens in London bring new life to railway wasteland
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
World Cup Experience and Sonic Foundation Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding SSRIs and Their Mechanism
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Synapses
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Learning Styles and Effective Study Strategies
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

18 questions
Mendelian Genetics
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Cell Cycle and mitosis
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Plant structures and tropisms
Quiz
•
9th Grade

55 questions
Category2 SPRING 2026 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

100 questions
*NEW Biology Benchmark 1 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th Grade

72 questions
#Category 4 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade