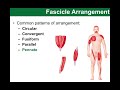
Muscle Fiber Arrangements and Functions
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Physical Ed
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary reason for studying muscle fiber arrangements?
To understand muscle color
To determine muscle strength
To gain insights into muscle names and functions
To measure muscle length
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which muscle is an example of a circular fiber arrangement?
Pectoralis major
Sartorius
Orbicularis oris
Biceps brachii
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a convergent fiber arrangement, how do the fibers typically converge?
In parallel lines
From a broad origin to a narrow insertion
In concentric circles
From a narrow origin to a broad insertion
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What shape are fusiform muscles typically associated with?
Circular
Spindle-shaped
Triangular
Flat
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which muscle is an example of a parallel fiber arrangement?
Pectoralis major
Sartorius
Deltoid
Rectus femoris
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the defining characteristic of pennate muscle fibers?
They attach obliquely to a central tendon
They run parallel to the muscle's long axis
They form concentric circles
They converge from a broad origin
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a unipennate muscle, how do the fibers attach to the tendon?
In a parallel pattern
In a circular pattern
Only on one side of the tendon
On both sides of the tendon
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Understanding Carbohydrates and Fiber
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Types and Characteristics
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms and Structures
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Physiology and Neuromuscular Junctions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

9 questions
Total Internal Reflection in Optical Fibers
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Fibers and Endurance Performance
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Muscle Fiber Types Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Exploring the Muscular System and Sliding Filament Theory
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
9/11 Experience and Reflections
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

9 questions
Tips & Tricks
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Scientific method
Interactive video
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Section 3 - Macromolecules and Enzymes
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade