Energy Transfer and Efficiency Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Mathematics
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the three main topics covered in this video?
Fossil fuels, Sankey diagrams, and efficiency
Nuclear energy, Sankey diagrams, and efficiency
Fossil fuels, kinetic energy, and potential energy
Nuclear energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a fossil fuel power plant, what is the primary form of energy produced by burning the fuel?
Thermal energy
Potential energy
Electrical energy
Kinetic energy
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of steam in a fossil fuel power plant?
To generate nuclear reactions
To absorb thermal energy
To drive the turbine
To cool down the system
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
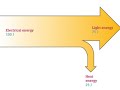
In a Sankey diagram, what does the width of an arrow represent?
The type of energy
The speed of energy transfer
The amount of energy
The direction of energy flow
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What percentage of energy is typically considered useful in a Sankey diagram?
10%
20%
35%
50%
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is efficiency calculated in physics?
Useful power divided by total input power
Total input power divided by useful power
Total output power divided by useful power
Useful power divided by total output power
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the symbol commonly used to represent efficiency?
λ (lambda)
ε (epsilon)
μ (mu)
η (eta)
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
2 Step Word Problems
Quiz
•
KG - University

20 questions
Comparing Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Latin Bases claus(clois,clos, clud, clus) and ped
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

7 questions
The Story of Books
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Exit Check 1.6 - Constant Velocity
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 1.7 - Graphing
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 2.1 - 1st Law
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Conservation of Energy
Quiz
•
11th Grade

11 questions
Conservation of Momentum: Physics in Motion Video
Interactive video
•
10th Grade

25 questions
Energy Quiz 5.1 Review 2026 Version
Quiz
•
11th Grade

35 questions
PA: Semester Knowledge Check
Quiz
•
11th Grade