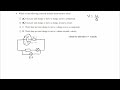
Understanding Potential Difference and EMF
Interactive Video
•
Physics
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of modeling a real cell as an ideal cell with EMF and internal resistance?
To reduce the cost of the cell
To simplify calculations by ignoring internal resistance
To better understand the behavior of real cells
To increase the efficiency of the cell
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is electromotive force (EMF) defined?
The energy transferred to electrical energy per unit charge
The force exerted by a cell on a charge
The voltage across a single component
The resistance of a cell
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following best describes terminal potential difference?
The voltage across the internal resistance
The energy lost as heat in the cell
The electrical energy transferred to other forms per unit charge in external components
The total voltage a cell can provide
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the potential difference across a single component?
The total voltage a cell can provide
The voltage across all external components
The work done per unit charge to move a charge across the component
The energy lost as heat in the internal resistance
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the EMF of a cell related to the work done in a circuit?
It is the work done to overcome the internal resistance
It is the work done per unit charge to move a charge around the circuit
It is the work done to move a charge across a single component
It is the work done to dissipate energy as heat
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the energy not transferred to external components in a circuit?
It is converted back to chemical energy
It is lost to the environment
It is dissipated as heat in the internal resistance
It is stored in the cell
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
If a cell has an EMF of 6 volts and the terminal potential difference is 5 volts, what is the voltage lost in the internal resistance?
4 volts
1 volt
2 volts
3 volts
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

16 questions
Coulomb's Law
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Heat, Thermal Energy, and Temperature
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
unit 10 -- electric forces and fields
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Diffraction, Reflection, Refraction
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

11 questions
Conservation of Momentum: Physics in Motion Video
Interactive video
•
10th Grade