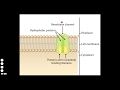
ATP and ABC Transporters Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
9 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of ATP in ABC Transporters?
To bind with toxins
To act as a nutrient
To drive membrane transport
To provide structural support
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of ABC Transporter is responsible for carrying nutrients into the cell?
Efflux Transporters
Influx Transporters
Membrane Transporters
Nucleotide Transporters
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What do efflux ABC Transporters primarily expel from the cell?
Water and salts
Proteins and lipids
Antibiotics and toxins
Sugars and amino acids
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What forms the membrane channel in an ABC transporter?
Two hydrophobic proteins
Two nucleotide proteins
Two hydrophilic proteins
Two cytoplasmic proteins
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What role do solute binding proteins play in the transport process?
They block solute entry
They degrade solutes
They provide energy for transport
They increase transport efficiency
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do solute binding proteins affect the channel protein?
They cause it to close
They trigger a structural change
They dissolve it
They strengthen it
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to ATP during the transport process?
It is converted to glucose
It remains unchanged
It is hydrolyzed
It is synthesized
8.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is released after ATP is hydrolyzed in the transport process?
Glucose and water
ADP and inorganic phosphate
Proteins and lipids
Sugars and amino acids
9.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the transporter after the solute enters the cell?
It remains open
It breaks down
It returns to its resting state
It becomes inactive
Similar Resources on Wayground

3 questions
Scientists Discover Potential Breakthrough in Malaria Treatment: Targeting the Glucose Transporter Protein
Interactive video
•
KG - University

2 questions
Scientists Discover Potential Breakthrough in Malaria Treatment: Targeting the Glucose Transporter Protein
Interactive video
•
KG - University

11 questions
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and Their Role in Cell Signaling
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

2 questions
Protein functions in the human body
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Cell Membrane Transport Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Transport Mechanisms in Cells
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Transport Proteins and Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Insulin and Its Mechanism
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

55 questions
CHS Student Handbook 25-26
Quiz
•
9th Grade

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Chaffey
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
PRIDE
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
6-8 Digital Citizenship Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

18 questions
Characteristics of Living Things
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

12 questions
Macromolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Biomolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

27 questions
Flinn - Lab Safety Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
10th Grade

19 questions
Scientific Method
Quiz
•
10th Grade

7 questions
Viruses Replication
Lesson
•
12th Grade