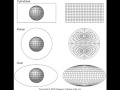
Map Projections and Their Characteristics
Interactive Video
•
Geography
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why are maps considered a useful substitute for the real world?
They can show the entire planet at once.
They allow us to compute the actual size of features.
They eliminate the need for physical travel.
They provide a 3D view of the Earth.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a graphic scale on a map help with?
Understanding the Earth's rotation.
Visualizing the curvature of the Earth.
Calculating the volume of geographical features.
Directly comparing feature sizes and distances.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a representative fraction (RF) in map scales?
A statement comparing units on the map to units on Earth.
A graphic representation of distances.
A ratio between map distance and Earth distance.
A method to visualize map features.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the expanse of the real world shown on a map affect its geometric accuracy?
Larger areas increase accuracy.
Smaller areas decrease accuracy.
It has no effect on accuracy.
Larger areas decrease accuracy.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when a plane is placed in contact with a sphere?
The surfaces merge without distortion.
The distance between surfaces remains constant.
The distance decreases with distance from the contact point.
The distance increases with distance from the contact point.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the first step in creating a map projection?
Reducing the Earth to a small globe.
Choosing a projection surface.
Flattening the globe.
Centering the projection on the area of interest.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which projection surfaces can be flattened without distortion?
Cone, sphere, and cylinder.
Cylinder, sphere, and plane.
Sphere, cone, and plane.
Cone, cylinder, and plane.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
3.7 Unit One Review Video
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Steven Payne's Pilgrimage Journey
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Plate Boundaries and Tsunami Prediction
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Earth's Surface and Celestial Features
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Selfie Distortion and Perception Effects
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Map Projections and Their Characteristics
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Maps and Cartography Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Africa: Geography and Demographics
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Geography

17 questions
Continents and Oceans
Lesson
•
5th - 9th Grade

26 questions
AP Human Geography Unit 1
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Population Pyramid
Quiz
•
9th Grade

18 questions
PEGS World Geography ReviewVocabulary Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

9 questions
Weather vs Climate
Quiz
•
3rd - 9th Grade

28 questions
APHUG UNIT 1
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

50 questions
All 50 States - Locations
Quiz
•
KG - University

10 questions
Five Themes of Geography
Quiz
•
KG - University