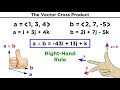
Cross Product of Vectors Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Physics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Liam Anderson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the result of a dot product between two vectors?
A tensor
A matrix
A scalar
A vector
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which method is used to find the cross product of two vectors?
Matrix inversion
Matrix subtraction
Determinant of a matrix
Matrix addition
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the direction of the cross product of two vectors?
Perpendicular to the original vectors
In the same direction as vector A
In the same direction as vector B
Parallel to the original vectors
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you determine the direction of a cross product using your hand?
Right-hand rule
Left-hand rule
Index finger rule
Thumb rule
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the cross product of a vector with itself?
A vector with half the magnitude
A zero vector
A unit vector
A vector with double the magnitude
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the magnitude of the cross product of two vectors related to?
The volume of the parallelogram they form
The sum of the vectors
The area of the parallelogram they form
The difference of the vectors
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the cross product of two parallel vectors?
It becomes a zero vector
It becomes a scalar
It becomes a matrix
It becomes a unit vector
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Resolution of Vectors
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Orthogonal and Orthonormal Vectors
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Learn to find the angle between two vectors
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Calculus III: Two Dimensional Vectors (Level 4 of 13)
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Vectors and Planes
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Vector Operations and Triangle Area
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Vector Multiplication: Dot and Cross Products Explained
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Vector Concepts and Operations
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
9/11 Experience and Reflections
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

9 questions
Tips & Tricks
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Calculating Net Force
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Using Scalar and Vector Quantities
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acceleration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

5 questions
Reading Motion Graphs
Lesson
•
8th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Distance Time Graphs
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

13 questions
Velocity Graphs Position vs. Time
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade