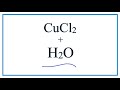
Copper II Chloride Reactions and Properties
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Lucas Foster
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of compound is formed when copper and chlorine combine?
Molecular compound
Metallic compound
Ionic compound
Covalent compound
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is it important to check a solubility table for copper II chloride?
To check its reactivity with air
To find its boiling point
To confirm its solubility in water
To determine its melting point
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What ions are formed when copper II chloride dissolves in water?
Copper ions and oxygen ions
Chlorine ions and hydrogen ions
Copper ions and chloride ions
Chloride ions and sodium ions
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the charge on the copper ion in the dissociation of copper II chloride?
2-
1-
2+
1+
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How many chloride ions are present for each copper ion in the dissociation?
Four
Two
One
Three
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the 'aq' notation signify in a chemical equation?
Aqueous or dissolved in water
Gaseous state
Liquid state
Solid state
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is water not written on the product side of the equation?
Because it is not involved in the reaction
Because it is a solid
Because it evaporates immediately
Because it is already represented by 'aq'
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

7 questions
Cobalt II Chloride and Solubility
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Barium Chloride Properties and Reactions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Electrolytes and Iron(II) Chloride
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Sodium Fluoride and Electrolytes Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Balancing Chemical Reactions and Equations
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Chemical Reactions and Replacements
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Zinc and Copper(II) Chloride Reactions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Net Ionic Equations and Spectator Ions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
SR&R 2025-2026 Practice Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

30 questions
Review of Grade Level Rules WJH
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

6 questions
PRIDE in the Hallways and Bathrooms
Lesson
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Lab Safety and Lab Equipment
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

12 questions
elements, compounds, and mixtures
Quiz
•
9th Grade

12 questions
Significant figures
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Unit 1b Lesson 1 Quick Check
Quiz
•
9th Grade

12 questions
significant figures and calculations
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

20 questions
12.2 Scientific Notation and Significant Figures
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Significant Figures
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade

12 questions
Atomic Structure and isotopes
Quiz
•
10th Grade