
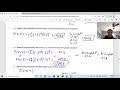
Probability and Distributions Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Thomas White
FREE Resource
Read more
8 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary focus of the video tutorial on distributions?
Understanding the history of distributions
Learning to use calculators for distribution calculations
Exploring the philosophical aspects of probability
Discussing the ethical implications of statistics
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the 'B' in the BINS acronym for binomial settings stand for?
Bounded variables
Binary outcomes
Balanced trials
Basic probability
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the free throw example, what is the probability of success for each trial?
80%
50%
60%
70%
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the binomial PDF function calculate?
The average number of successes
The probability of exactly a specific number of successes
The variance of the distribution
The probability of a range of outcomes
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which formula is used to calculate the mean of a binomial distribution?
n + P
n / P
n - P
n * P
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the key difference between binomial and geometric distributions?
Geometric distributions count trials until the first success
Binomial distributions focus on the first success
Binomial distributions have variable probabilities
Geometric distributions have a fixed number of trials
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the Monopoly example, what is the probability of rolling doubles?
1/4
1/3
1/6
1/2
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Understanding Infinite Geometric Series
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Quadratic Equation and Completing the Square
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Autochess Gameplay Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Understanding the Art and History of Safavid Carpets
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Monohybrid Crosses and Punnett Squares Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Probability Concepts and Applications Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Probability Concepts Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

20 questions
Graphing Inequalities on a Number Line
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Exponent Properties
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Combine Like Terms and Distributive Property
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Function or Not a Function
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

10 questions
Factor Quadratic Expressions with Various Coefficients
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Elijah McCoy: Innovations and Impact in Black History
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

21 questions
Factoring Trinomials (a=1)
Quiz
•
9th Grade

5 questions
Triangle Congruence Theorems
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade