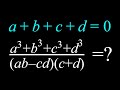
Evaluating Methods for Cubing Expressions
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Thomas White
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial condition given in the problem?
a + b + c + d = 2
a + b + c + d = 0
a + b + c + d = 1
a + b + c + d = -1
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the expression that needs to be evaluated?
a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + d^3 divided by (ab + cd)(c - d)
a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + d^3 divided by (ab - cd)(c + d)
a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + d^3 divided by (ab - cd)(c - d)
a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + d^3 divided by (a + b)(c + d)
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the first method primarily based on?
Geometric transformations
Algebraic manipulations
Graphical representation
Numerical calculations
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the alternative to cubing the entire expression in the first method?
Factoring the expression
Using a different identity
Cubing each term separately
Squaring the expression
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which identity is used in the first method for cubing?
Exponential identity
Trigonometric identity
Binomial theorem
Pythagorean identity
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the result of the first method?
The expression equals 3
The expression equals 1
The expression equals 0
The expression equals 2
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main idea behind the second method?
Numerical approximation
Graphical representation
Using a different algebraic identity
Using specific values for variables
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

20 questions
Graphing Inequalities on a Number Line
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Exponent Properties
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
Combine Like Terms and Distributive Property
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Function or Not a Function
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

10 questions
Factor Quadratic Expressions with Various Coefficients
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Elijah McCoy: Innovations and Impact in Black History
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

21 questions
Factoring Trinomials (a=1)
Quiz
•
9th Grade

5 questions
Triangle Congruence Theorems
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade