What is the initial problem discussed in the video?
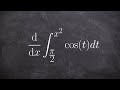
Fundamental Theorem and Chain Rule
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Thomas White
FREE Resource
Read more
15 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Solving a differential equation
Integrating a function from x^2 to Pi halves
Finding the limit of a sequence
Calculating the area under a curve
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial setup for the integration problem?
Finding the derivative of a trigonometric function
Integrating from x^2 to Pi halves
Differentiating a polynomial
Solving a quadratic equation
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the integral evaluated from in the problem?
Pi to 2Pi
x^2 to Pi halves
0 to 1
1 to e
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is it important to understand the process of integration?
To solve algebraic equations
To memorize formulas
To apply the correct method in different scenarios
To avoid using calculators
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus allow us to do?
Differentiate functions easily
Find the roots of polynomials
Solve linear equations
Rewrite integrals in a simpler form
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when the upper bound of an integral is a function?
The process of differentiation changes
The integral can be solved directly
The function must be linear
The integral becomes undefined
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is emphasized about the upper bound in the integration process?
It should be ignored during integration
It can be a function, affecting differentiation
It must be greater than the lower bound
It should always be a constant
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Quizizz

11 questions
Integration Concepts and Techniques
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Integrals and Riemann Sums
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Analyzing Derivatives and Concavity
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Calculus Concepts and Trigonometric Identities
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Differentiation and Integration Concepts
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Calculus: Derivatives and Integrals
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Integration and Differentiation Concepts
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Quizizz

15 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
4th Grade

25 questions
SS Combined Advisory Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Week 4 Student In Class Practice Set
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

40 questions
SOL: ILE DNA Tech, Gen, Evol 2025
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
NC Universities (R2H)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
June Review Quiz
Quiz
•
Professional Development

20 questions
Congruent and Similar Triangles
Quiz
•
8th Grade

25 questions
Triangle Inequalities
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

40 questions
Week 4 Student In Class Practice Set
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Triangle Inequalities
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Right Triangles: Pythagorean Theorem and Trig
Quiz
•
11th Grade

45 questions
Week 3.5 Review: Set 1
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

17 questions
High School Survival Guide
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade