Understanding Variable Charged Cations and Naming Ionic Compounds
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard

Nancy Jackson
FREE Resource
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the two main objectives of today's lesson?
Understanding covalent bonding and molecular geometry
Exploring the properties of gases and their laws
Studying the history of the periodic table and its elements
Learning about variable charged cations and naming ionic compounds
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
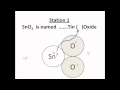
What is the correct name for the compound MGO?
Magnesium Fluoride
Magnesium Oxide
Magnesium Chloride
Magnesium Sulfide
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the periodic table contains elements with variable charges?
The f-block
The d-block and elements under the staircase
The s-block
The p-block
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why must the total positive charge equal the total negative charge in ionic compounds?
To ensure the compound is electrically neutral
To decrease the compound's solubility
To make the compound more reactive
To increase the compound's melting point
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How are variable charged cations indicated in the names of ionic compounds?
Using superscripts
Using Roman numerals
Using subscripts
Using Greek letters
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the charge on copper in copper(II) chloride?
2+
1+
3+
4+
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the compound Sn3N2, what is the charge on each tin atom?
4+
2+
1+
3+
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Formative 3BC: Ionic v Covalent Bonds
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Stoichiometry Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Mixed Bonding Naming
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Naming & Writing Chemical Formulas
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Practice: E-Con, Orbital Notation, Noble Gas Notation
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Covalent Bonding
Quiz
•
10th Grade