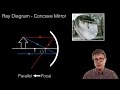
Mirror Properties and Image Formation
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Easy
Liam Anderson
Used 15+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of a mirror in a telescope?
To focus light
To absorb light
To emit light
To refract light
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of mirror is described as 'going into a cave'?
Concave mirror
Spherical mirror
Convex mirror
Plane mirror
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a plane mirror, what kind of image is formed?
Virtual and inverted
Real and upright
Virtual and upright
Real and inverted
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the rule for the angle of incidence in reflection?
It is equal to the angle of reflection
It is twice the angle of reflection
It is always zero
It is equal to the angle of refraction
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the focal point in a concave mirror?
The point where the mirror is thickest
The point where light rays parallel to the mirror converge
The center of the mirror
The point where light rays diverge
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the image appear when an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror?
Same size and upright
Smaller and inverted
Same size and inverted
Larger and upright
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the image when an object is placed inside the focal length of a concave mirror?
The image becomes real and inverted
The image becomes virtual and upright
The image disappears
The image becomes smaller and inverted
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

16 questions
Coulomb's Law
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Heat, Thermal Energy, and Temperature
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
unit 10 -- electric forces and fields
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Diffraction, Reflection, Refraction
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

11 questions
Conservation of Momentum: Physics in Motion Video
Interactive video
•
10th Grade