
Uniform Circular Motion
Authored by Lisa Thompson
Science
11th Grade
NGSS covered

AI Actions
Add similar questions
Adjust reading levels
Convert to real-world scenario
Translate activity
More...
Content View
Student View
15 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
A toy car is following a circular path with a constant speed of v=3 m/s . If the radius of the circular path is 1 m, find The centripetal acceleration of the car
30 m/s2
3 m/s2
9 m/s2
6 m/s2
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
A 10kg car travels at a constant speed of 20.0 m/s around a horizontal circular track. Which diagram correctly represent the direction of the car's velocity (v) and the direction of the centripetal force (Fc) acting on the car at a particular moment?
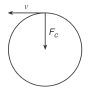
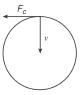
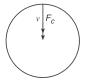
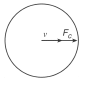
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
The time taken for one complete circuit is called the...
Period
Frequency
Angular velocity
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS4-1
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

Centripetal acceleration always points
in the direction of the object's motion
in the opposite direction of the object's motion
towards the center of the circle
towards the outside of the circle
Tags
NGSS.HS-ESS1-4
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

You swing a bucket of water attached to a string in a circle above your head. What keeps the water in the bucket?
Friction
Centripetal Force
Gravity
Inertia
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
Centrifugal force is a ______
force that pushes you to the outside of a circle during uniform circular motion.
fictitious force that is really just the linear momentum of an object in uniform circular motion.
The force that keeps the planets in orbit
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
what is the centripetal acceleration formula?
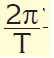
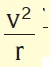
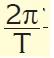
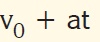
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS2-1
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

20 questions
LEMAK DAN GETAH
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

12 questions
Matter everywhere!
Quiz
•
2nd Grade - University

14 questions
Metabolism and Chloroplast Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade - University

14 questions
General knowledge quiz
Quiz
•
5th Grade - Professio...

10 questions
Nutrient Requirement of Plants
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
P2 Energy transfer by heating
Quiz
•
9th - 11th Grade

10 questions
Digestive System
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Taller 2 75% 2020A
Quiz
•
8th - 11th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Figurative Language Review
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

14 questions
Natural Selection and Adaptation
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

38 questions
Water Cycle and Groundwater
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

12 questions
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

12 questions
Homeostasis: Positive and Negative Feedback Loops
Interactive video
•
11th Grade

13 questions
Amoeba Sisters: Biomolecules
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

60 questions
2025 Genetics Test Study Guide
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Understand Cell Functions and Organelles
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
Explore Cell Cycle Stages and Mitosis
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade


