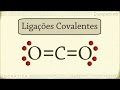
Covalent Bonds and Molecular Polarity
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Sophia Harris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the three main types of intermolecular forces?
Hydrogen, Van der Waals, and Dipole-Dipole
Ionic, Covalent, and Metallic
Covalent, Metallic, and Hydrogen
Ionic, Covalent, and Van der Waals
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why are covalent bonds considered stable?
Because they share protons
Because they share neutrons
Because they share nuclei
Because they share electrons
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a Lewis dot structure, how is a single covalent bond represented?
As a pair of dots
As a single line
As a double line
As a triple line
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the electron configuration of hydrogen in a covalent bond with fluorine?
Same as Argon
Same as Neon
Same as Helium
Same as Krypton
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of bond is formed when two atoms share electrons equally?
Ionic bond
Polar covalent bond
Non-polar covalent bond
Metallic bond
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which molecule is an example of a non-polar covalent bond?
H2
CO2
H2O
NH3
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What causes a molecule to be polar?
Unequal sharing of electrons
Equal sharing of electrons
Unequal sharing of neutrons
Equal sharing of protons
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Chemical Bonds
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Polarity in Chemical Bonds
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Polar Covalent Bonds
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Polar and Non-Polar Molecules
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
TED-Ed: How polarity makes water behave strangely - Christina Kleinberg
Interactive video
•
KG - University

11 questions
Understanding Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Molecular Polarity and Electronegativity Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Electronegativity in Organic Chemistry
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

40 questions
LSHS Student Handbook Review: Pages 7-9
Quiz
•
11th Grade

24 questions
Scientific method and variables review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Mental Health Vocabulary Pre-test
Quiz
•
9th Grade