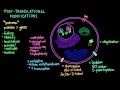
Post-Translational Modifications in Proteins
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary reason for the complexity of the human proteome compared to the genome?
Lack of protein diversity
The simplicity of the genome
Post-translational modifications
The presence of more genes than proteins
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a purpose of post-translational modifications?
Regulating protein localization
Decreasing protein diversity
Increasing protein stability
Altering protein activity
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Methylation primarily involves the transfer of which group to amino acid side chains?
Phosphate group
Acetyl group
Hydroxyl group
Methyl group
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of acetylation in histones?
To degrade proteins
To inhibit DNA replication
To promote transcription
To condense chromosomal structure
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Glycosylation involves the addition of which type of molecules to proteins?
Lipids
Sugars
Phosphates
Amino acids
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of lipidation in proteins?
To target proteins to specific membranes
To alter protein charge
To increase protein solubility
To degrade proteins
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Ubiquitination is primarily used for what purpose in cells?
Protein synthesis
Protein stabilization
Protein degradation
Protein folding
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Translation and Post-Translational Control
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Proteins
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Membrane Proteins Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Ribosome Termination by Release Factors
Interactive video
•
University

11 questions
Genetic Code and Translation Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Ubiquitination of Damaged Proteins
Interactive video
•
University

6 questions
JAK STAT Signaling Pathway: Regulation
Interactive video
•
University
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
SR&R 2025-2026 Practice Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

30 questions
Review of Grade Level Rules WJH
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

6 questions
PRIDE in the Hallways and Bathrooms
Lesson
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

15 questions
Properties of Water
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Lab Safety & Lab Equipment
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

26 questions
Quiz Week 2 REVIEW (8.29.25)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

29 questions
Cell Practice 2
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

19 questions
Body Cavities and Regions
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the 4 Major Macromolecules and Their Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

36 questions
TEKS 5C Cellular Transport Vocabulary
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade