
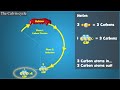
Calvin Cycle Concepts and Processes
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the two key products from the light reactions that are essential for the Calvin Cycle?
Chlorophyll and Sunlight
Oxygen and Glucose
ATP and NADPH
Carbon Dioxide and Water
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the carbon fixation phase, what enzyme is responsible for incorporating CO2 into an organic molecule?
Rubisco
ATP Synthase
NADP Reductase
Photosystem II
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the reduction phase, what is the main product formed that can be used to make sugars?
NADPH
RuBP
G3P
ATP
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the significance of G3P in the Calvin Cycle?
It is a waste product
It releases oxygen
It is used to make sugars
It absorbs light
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How many G3P molecules are needed to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin Cycle?
One
Six
Three
Five
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of ATP in the regeneration phase of the Calvin Cycle?
Supplies electrons
Absorbs light
Acts as a catalyst
Provides energy
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which phase of the Calvin Cycle involves the conversion of G3P back to RuBP?
Photosynthesis
Regeneration
Carbon Fixation
Reduction
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Cellular Respiration Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Transitioning from Fossil Fuels: Challenges and Pathways
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Proteins
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN: A new Uranium boom in the West?
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : A fire for democracy is burning in students hearts (activist)
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Quasars and the Milky Way
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Spider Mites: Life Cycle and Impact
Interactive video
•
7th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Designing Solutions Review
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

22 questions
Human Body Systems Overview
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
African American Impact in the 1980s
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Symbiotic Relationships
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Cladogram Practice
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
CFA #2 Unit 3 Human Body Systems (21.2 & 21.3)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade