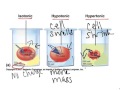
Cell Transport and Solutions Effects
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of cell transport?
To create new cells
To divide the cell into two
To produce energy for the cell
To move particles across the cell membrane
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In an isotonic solution, what happens to the water movement across the cell membrane?
Water moves equally in both directions
Water moves only out of the cell
Water moves only into the cell
Water does not move at all
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the water concentration inside a cell in an isotonic solution if the outside concentration is 75%?
100%
75%
25%
50%
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the effect of a hypotonic solution on a cell?
The cell shrinks
The cell swells
The cell remains the same size
The cell divides
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why does a cell swell in a hypotonic solution?
Because salt moves out of the cell
Because water moves into the cell
Because salt moves into the cell
Because water moves out of the cell
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the mass of a cell in a hypotonic solution?
It disappears
It increases
It decreases
It remains the same
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a hypertonic solution, what happens to the cell?
The cell shrinks
The cell bursts
The cell remains the same size
The cell swells
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Osmosis and Cell Interaction Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Transport Mechanisms and Processes
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Water Balance and Tonicity Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Tonicity: Exploring Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Solutions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cell Reactions to Hypotonic and Hypertonic Solutions Explained
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Osmosis and Solutions Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Osmosis and Cell Solutions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Membrane and Transport
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Section 3 - Macromolecules and Enzymes
Quiz
•
10th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade