What does Hooke's Law state about the relationship between stress and strain?
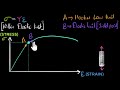
Stress-Strain Relationships in Materials
Interactive Video
•
Physics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Stress is proportional to strain beyond the elastic limit.
Stress is unrelated to strain.
Stress is proportional to strain within the elastic limit.
Stress is inversely proportional to strain.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to a material when it is stressed beyond the elastic limit?
It undergoes permanent deformation.
It becomes more elastic.
It returns to its original shape.
It breaks immediately.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a stress-strain graph, what does the linear region represent?
The fracture point.
The region where Hooke's Law is not applicable.
The plastic flow region.
The region where stress is proportional to strain.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the plastic flow region characterized by?
Decreasing stress and decreasing strain.
Constant stress and increasing strain.
Increasing stress and constant strain.
Constant stress and decreasing strain.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the ultimate tensile strength of a material?
The minimum stress a material can handle.
The maximum stress a material can handle without serious damage.
The stress at which a material breaks.
The stress at which a material returns to its original shape.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What phenomenon occurs when a material is stretched beyond its ultimate tensile strength?
Complete recovery.
Necking.
Increased elasticity.
Elastic deformation.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the fracture point in a stress-strain graph?
The point where the material breaks.
The point where the material reaches its ultimate tensile strength.
The point where the material starts to deform elastically.
The point where the material returns to its original shape.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Quizizz

11 questions
Stress and Strain Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Tensile and Compressive Stress Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Young's Modulus Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Excel Functions and Stress-Strain Analysis
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Thermal Stress and Material Properties
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Stress-Strain Relationship Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Young's Modulus and Stress
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring The Fundamentals Of Hooke's Law And Elasticity
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Quizizz

15 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Math Review - Grade 6
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
math review
Quiz
•
4th Grade

5 questions
capitalization in sentences
Quiz
•
5th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Juneteenth History and Significance
Interactive video
•
5th - 8th Grade

15 questions
Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
R2H Day One Internship Expectation Review Guidelines
Quiz
•
Professional Development

12 questions
Dividing Fractions
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

25 questions
Spanish preterite verbs (irregular/changed)
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Identify Slope and y-intercept (from equation)
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

10 questions
Juneteenth: History and Significance
Interactive video
•
7th - 12th Grade

8 questions
"Keeping the City of Venice Afloat" - STAAR Bootcamp, Day 1
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

26 questions
June 19th
Quiz
•
4th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Distance, Midpoint, and Slope
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Figurative Language Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade

27 questions
STAAR English 1 Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade