Molecular Geometry and Polarity of H2S
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Olivia Brooks
FREE Resource
Read more
7 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What initial observation is made about the Lewis structure of H2S?
It has no lone pairs.
It is a linear molecule.
It appears symmetrical.
It appears asymmetrical.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What theory is used to understand the arrangement of electrons in H2S?
Molecular Orbital Theory
Valence Bond Theory
Crystal Field Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
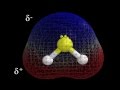
In the molecular geometry of H2S, what color represents sulfur?
Red
Blue
Yellow
White
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do the lone pairs of electrons affect the shape of the H2S molecule?
They have no effect.
They make it linear.
They push the hydrogen atoms upward.
They push the hydrogen atoms downward.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What indicates that H2S is a polar molecule?
It has no poles.
It has two positive poles.
It has two negative poles.
It has a positive and a negative pole.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the significance of the blue and red colors in the polarity explanation of H2S?
Both are neutral.
Blue is negative, red is positive.
Blue is positive, red is negative.
Both are positive.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is suggested as a better way to draw the Lewis structure of H2S?
As a linear molecule
With lone pairs at the bottom
With no lone pairs
Based on its molecular geometry
Similar Resources on Wayground

7 questions
Ozone Polarity and Molecular Geometry
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

7 questions
Polarity and Structure of SO2
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
C2H4 Non-Polarity and Structure
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Polarity of O2 Molecule Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
CBr4 Molecular Properties and Structure
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Electronegativity and Molecular Polarity
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Molecular Polarity and Electronegativity
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

9 questions
Polarity and Properties of CH3F
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

24 questions
Scientific method and variables review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Mental Health Vocabulary Pre-test
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Points, Lines, Planes
Quiz
•
9th Grade