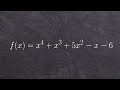
Polynomial Factorization and Zeros
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Thomas White
FREE Resource
Read more
25 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial step in determining the potential rational zeros of a polynomial?
List all factors of the middle term.
List all factors of both the constant term and the leading coefficient.
List all factors of the leading coefficient.
List all factors of the constant term.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of listing all factors of the constant term and leading coefficient?
To determine potential rational zeros.
To graph the polynomial.
To find the degree of the polynomial.
To simplify the polynomial.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you test potential factors if you don't have a calculator?
Use only positive factors.
Use a graphing method to visualize the zeros.
Start with positive one and then test negative one, then two, and so on.
Start with the largest factor and work downwards.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are two methods mentioned for checking if a number is a zero of a polynomial?
Graphing and using a calculator.
Synthetic division and the remainder theorem.
Using the quadratic formula and graphing.
Factoring and completing the square.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the remainder theorem state?
The remainder is irrelevant in factorization.
If the remainder is non-zero, the divisor is a factor.
If the remainder is zero, the divisor is a factor.
The remainder is always zero for any divisor.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a zero remainder in synthetic division indicate?
The polynomial is quadratic.
The polynomial is prime.
The divisor is a factor.
The divisor is not a factor.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the factor theorem state about a polynomial?
The polynomial has no real roots.
The polynomial is always factorable.
If a polynomial is divisible by a binomial, the remainder is non-zero.
If a polynomial is divisible by a binomial, the remainder is zero.
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

20 questions
Graphing Inequalities on a Number Line
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

18 questions
SAT Prep: Ratios, Proportions, & Percents
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

12 questions
Exponential Growth and Decay
Quiz
•
9th Grade

12 questions
Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
Quiz
•
10th Grade

12 questions
Add and Subtract Polynomials
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Combine Like Terms and Distributive Property
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Function or Not a Function
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

10 questions
Elijah McCoy: Innovations and Impact in Black History
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade