
Muscle Contraction Mechanisms and Structures
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
Olivia Brooks
Used 4+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the sarcolemma in a muscle fiber?
The contractile unit of a muscle fiber
The cytoplasm of a muscle fiber
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber
The endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle fiber
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are myofibrils primarily responsible for in a muscle fiber?
Providing energy
Storing calcium
Contracting the muscle
Transporting nutrients
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
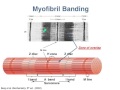
Which bands in a myofibril are associated with the striated appearance of skeletal muscle?
H bands and C bands
A bands and I bands
Z bands and M bands
X bands and Y bands
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the protein titin in muscle fibers?
To form the Z line
To bind calcium ions
To provide energy for contraction
To anchor myosin filaments and help muscles return to resting length
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of troponin in muscle contraction?
To cover actin binding sites
To form the M line
To change shape and move tropomyosin
To bind to ATP
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the sliding filament model, what happens when myosin heads bind to actin?
The Z discs move apart
The sarcomere shortens
The muscle fiber elongates
The I band lengthens
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the zone of overlap in a sarcomere?
The area where actin and myosin filaments overlap
The area with no filaments
The area with only myosin filaments
The area with only actin filaments
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis and Its Management
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Heart Healing After Myocardial Infarction
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
DNA Profiling and Analysis Quiz
Interactive video
•
8th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Posterior Scapular Region
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Heart Failure Treatments Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Healthy Nervous and Endocrine Systems: Caring for the Endocrine System
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Muscle Contraction Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

18 questions
Mendelian Genetics
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Cell Cycle and mitosis
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Plant structures and tropisms
Quiz
•
9th Grade

55 questions
Category2 SPRING 2026 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

100 questions
*NEW Biology Benchmark 1 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th Grade

72 questions
#Category 4 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade