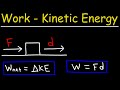
Work and Energy Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
Emma Peterson
Used 2+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the relationship between work and kinetic energy according to the work-energy theorem?
Work and kinetic energy are unrelated.
Kinetic energy is always greater than work.
Work done by the net force equals the change in kinetic energy.
Work is always greater than kinetic energy.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the derivation of the work-energy theorem, what is the formula for work when using Newton's Second Law?
Work = Mass x Velocity
Work = Mass x Acceleration x Displacement
Work = Force x Velocity
Work = Force x Time
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial speed of the 10 kg block in the example problem?
2 meters per second
4 meters per second
6 meters per second
8 meters per second
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the final speed of the 10 kg block calculated in the example problem?
Using the formula V final = Displacement / Time
Using the formula V final = Force / Mass
Using the formula V final squared = V initial squared + 2 x Acceleration x Displacement
Using the formula V final = V initial + Force x Time
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the work done by the 90 N force on the 10 kg block using the force-displacement method?
1600 joules
1700 joules
1900 joules
1800 joules
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the second example problem, what is the acceleration of the 5 kg block when a 40 N force is applied?
6 meters per second squared
7 meters per second squared
8 meters per second squared
9 meters per second squared
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the final velocity of the 5 kg block after 8 seconds?
72 meters per second
48 meters per second
56 meters per second
64 meters per second
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

5 questions
This is not a...winter edition (Drawing game)
Quiz
•
1st - 5th Grade

15 questions
4:3 Model Multiplication of Decimals by Whole Numbers
Quiz
•
5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
The Best Christmas Pageant Ever Chapters 1 & 2
Quiz
•
4th Grade

12 questions
Unit 4 Review Day
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Identify Iconic Christmas Movie Scenes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

18 questions
Kids Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
KG - 5th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

73 questions
IPC 2025 final review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

65 questions
Physics Semester 1 Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

17 questions
Free Body Diagrams
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Bill Nye Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
06c - Calculating Kinetic and Potential Energy
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
Physical Science Final Exam Review Part 1
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade