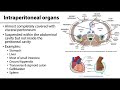
Retroperitoneal and Intraperitoneal Organs
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary focus of this video tutorial?
Defining terms related to gastrointestinal anatomy
Explaining cardiovascular anatomy
Discussing respiratory system functions
Analyzing muscular system dynamics
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is an example of an intraperitoneal organ?
Kidney
Liver
Ureter
Inferior vena cava
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Intraperitoneal organs are characterized by being:
Partially covered by visceral peritoneum
Not covered by peritoneum at all
Almost completely covered by visceral peritoneum
Completely outside the peritoneal cavity
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What distinguishes primary retroperitoneal organs from secondary ones?
Secondary organs are always retroperitoneal
Primary organs develop and remain retroperitoneal
Primary organs develop intraperitoneally
Secondary organs are never covered by peritoneum
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is a primary retroperitoneal organ?
Appendix
Pancreas
Kidney
Stomach
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Secondarily retroperitoneal organs initially develop as:
Intraperitoneal with no mesentery
Retroperitoneal with no mesentery
Subperitoneal with no mesentery
Intraperitoneal with a mesentery
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which organ is an example of a secondarily retroperitoneal organ?
Spleen
Gallbladder
Descending colon
Liver
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
TED-ED: How do fish make electricity? - Eleanor Nelsen
Interactive video
•
KG - University

11 questions
Serous Membranes and Body Cavities
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

2 questions
What's Causing That Stitch in Your Side?
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Intra-Abdominal Pressure Measurement Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Lymphatic System
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
What Is An Organ?
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
Nervous and Endocrine Systems: Summing Up
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Tu cuerpo: ¿qué constituye el cuerpo?
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Core 4 of Customer Service - Student Edition
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
What is Bullying?- Bullying Lesson Series 6-12
Lesson
•
11th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

12 questions
Macromolecules
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 2 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Cell Transport
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
AP Bio Insta-Review Topic 2.1*: Cell Structure - Subcellular Com
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Quick10Q: Organelles
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Investigation 13&2 Review
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

30 questions
Quiz Week 6 Review (9/26/25)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade