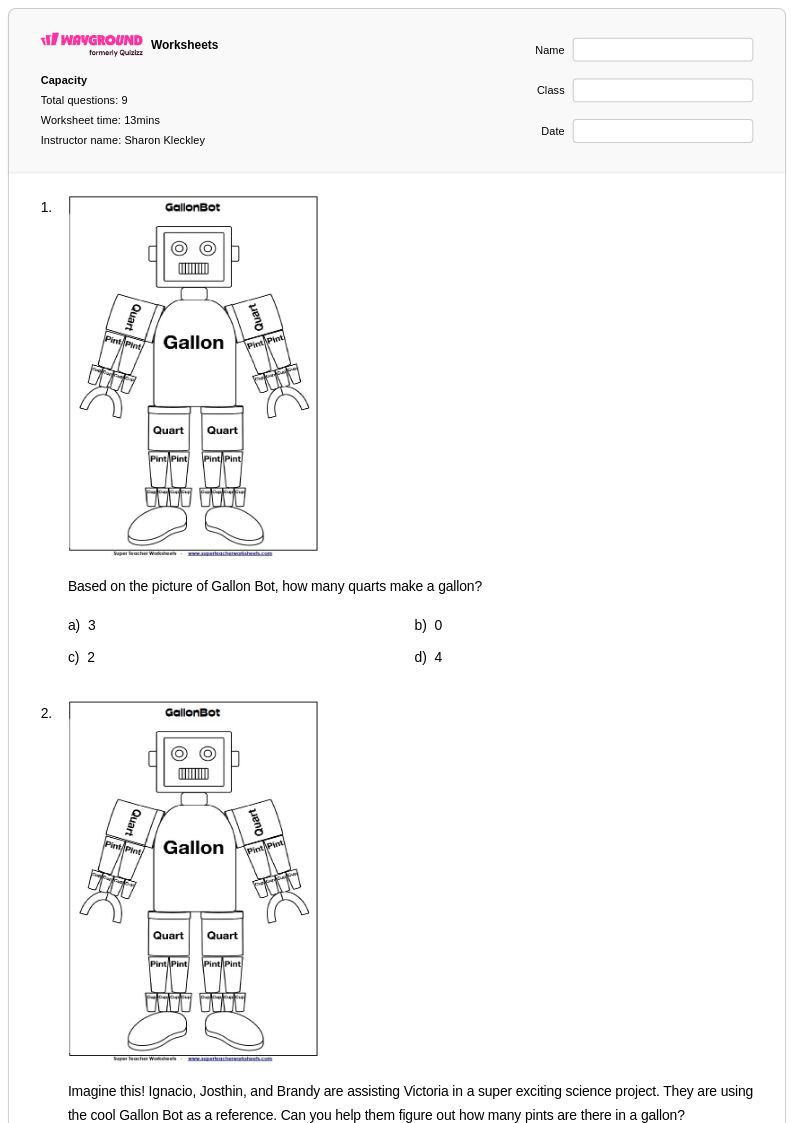
11 Q
3rd
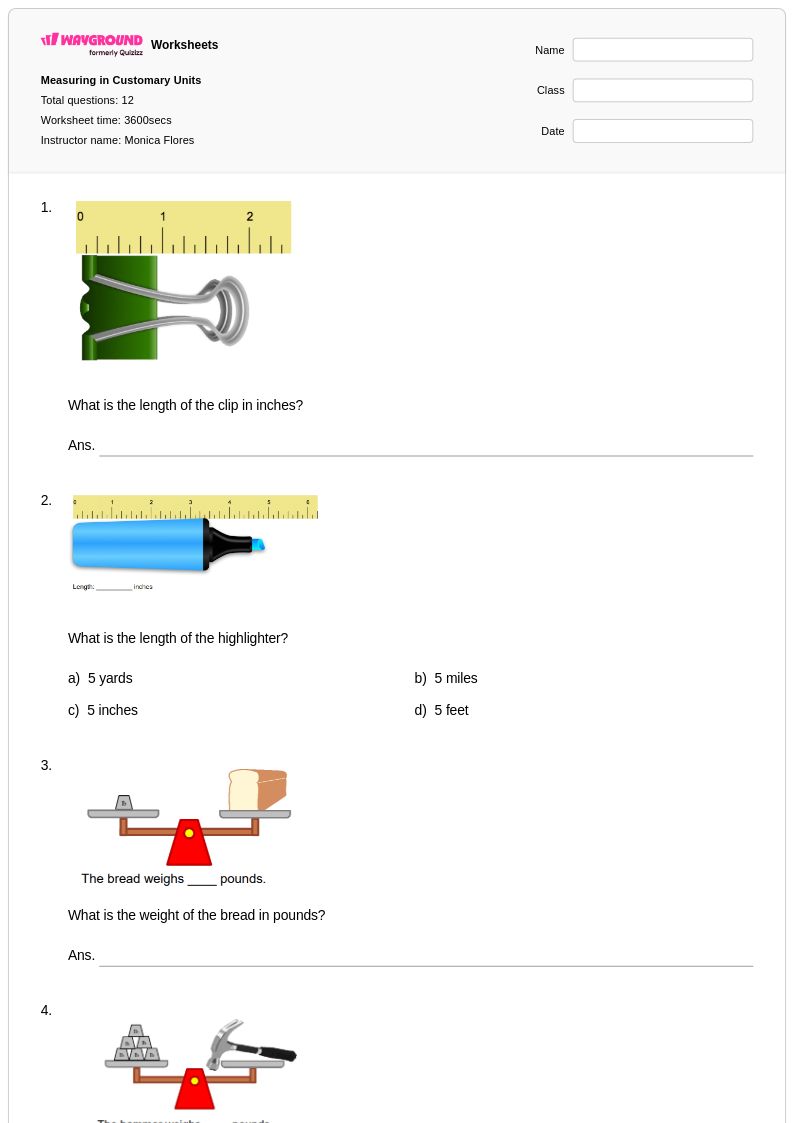
12 Q
3rd - 4th

5 Q
3rd - 4th

22 Q
3rd - 6th

15 Q
3rd - 4th
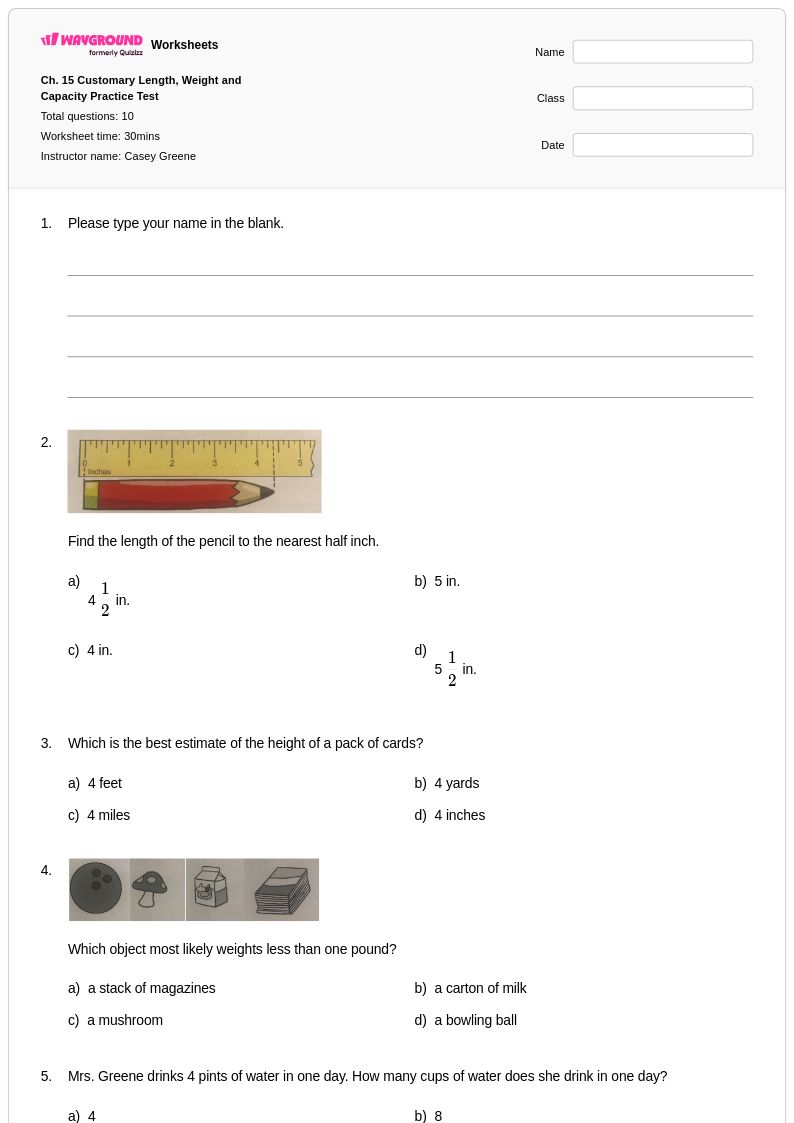
10 Q
3rd

13 Q
3rd
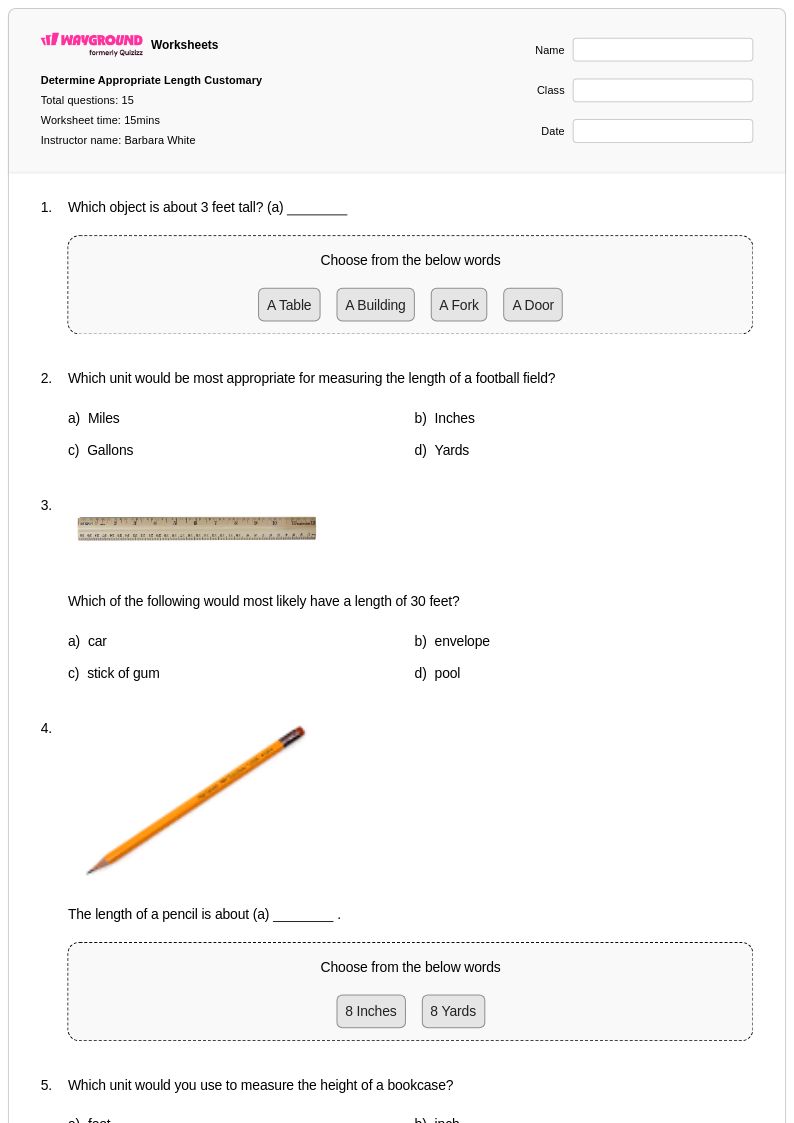
15 Q
3rd

20 Q
3rd - Uni

20 Q
3rd - Uni

18 Q
3rd - Uni

10 Q
3rd - 6th

11 Q
3rd

15 Q
3rd - Uni
15 Q
3rd

19 Q
3rd - 5th
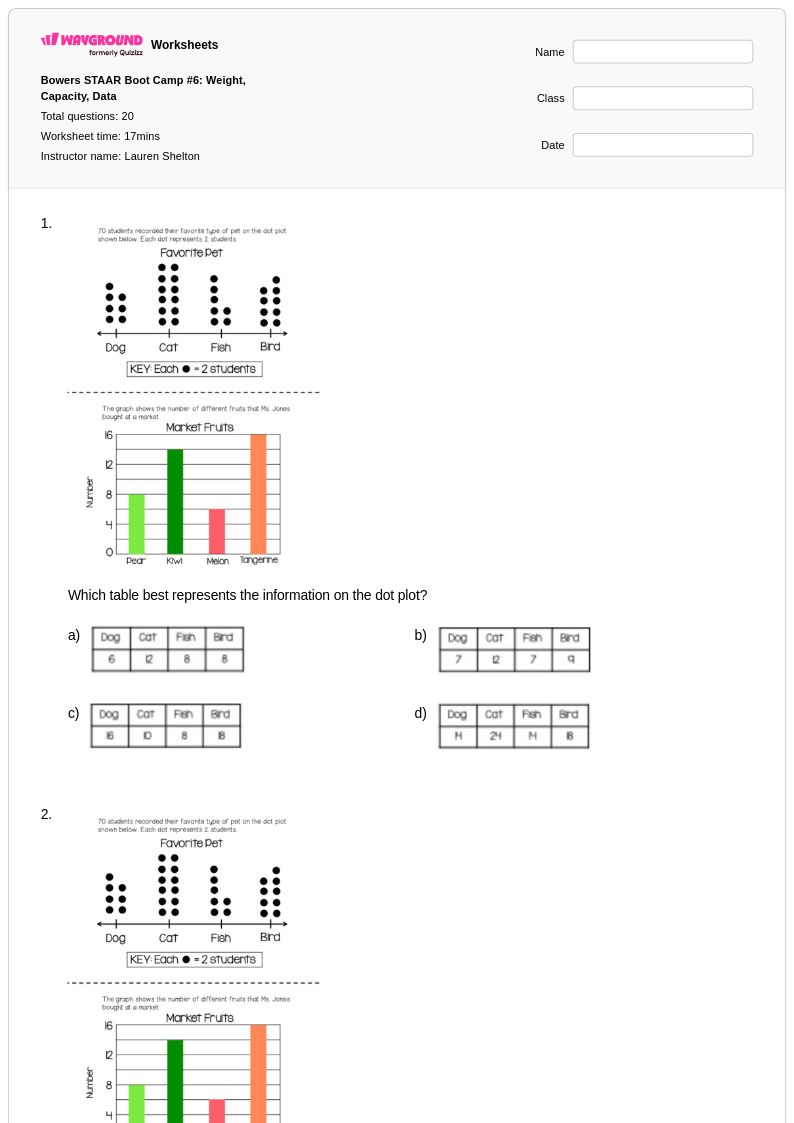
20 Q
3rd

20 Q
3rd

10 Q
3rd - 6th

21 Q
3rd - 4th

20 Q
3rd - Uni

96 Q
3rd

12 Q
3rd
12 Q
3rd
Explore Other Subject Worksheets for class 3
Explore printable Customary Capacity worksheets for Class 3
Customary capacity worksheets for Class 3 students available through Wayground (formerly Quizizz) provide comprehensive practice with fundamental measurement skills involving cups, pints, quarts, and gallons. These educational resources strengthen students' understanding of liquid measurement relationships and conversion techniques essential for mathematical literacy. The practice problems guide third-grade learners through systematic exploration of capacity relationships, helping them master concepts like recognizing that four cups equal one quart and four quarts equal one gallon. Each worksheet includes detailed answer keys that enable teachers to quickly assess student progress, while the free printable format makes these valuable resources accessible for classroom instruction, homework assignments, and independent study sessions.
Wayground (formerly Quizizz) empowers educators with millions of teacher-created customary capacity worksheets designed specifically for Class 3 mathematics instruction. The platform's advanced search and filtering capabilities allow teachers to locate materials aligned with state and national mathematics standards, ensuring curriculum coherence and academic rigor. These differentiation tools support diverse learning needs through customizable difficulty levels and problem types, making remediation and enrichment seamless within existing lesson plans. Teachers can access these resources in both printable pdf format for traditional classroom use and digital formats for interactive learning experiences, providing the flexibility needed for effective skill practice across various instructional settings and student learning preferences.
