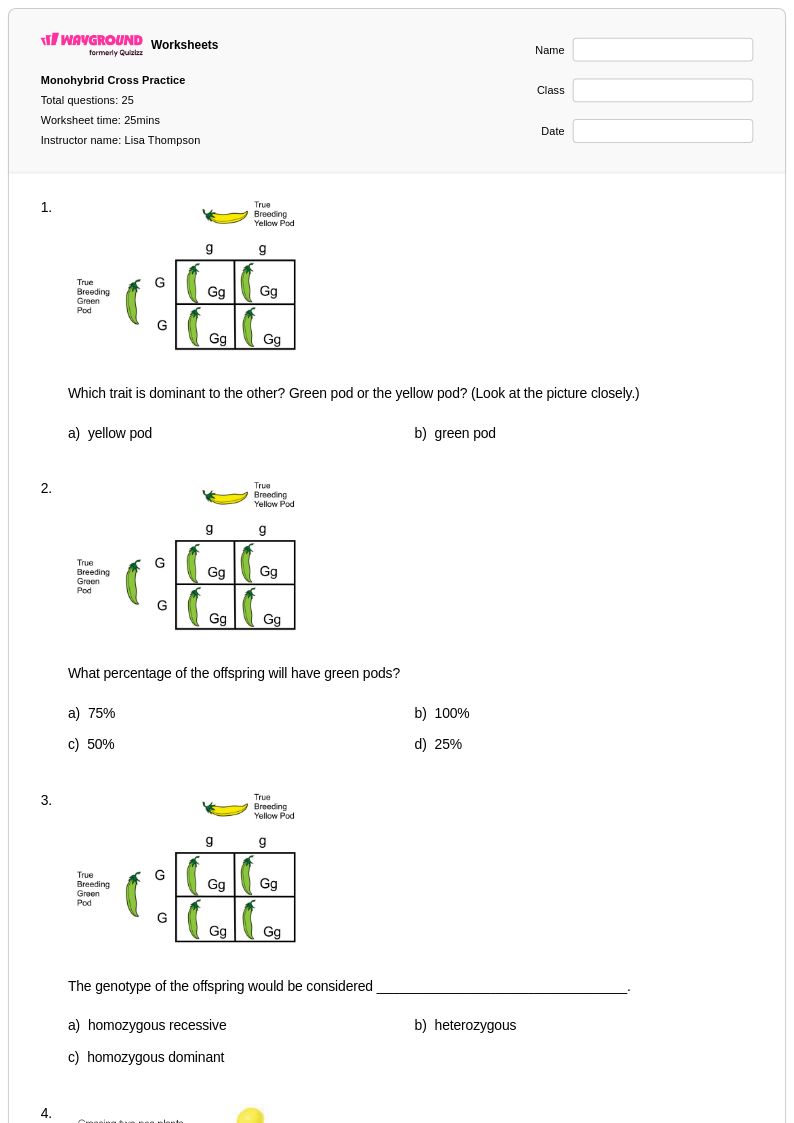
25 Q
9th - Uni

26 Q
Uni

20 Q
9th - 11th

37 Q
8th - 9th
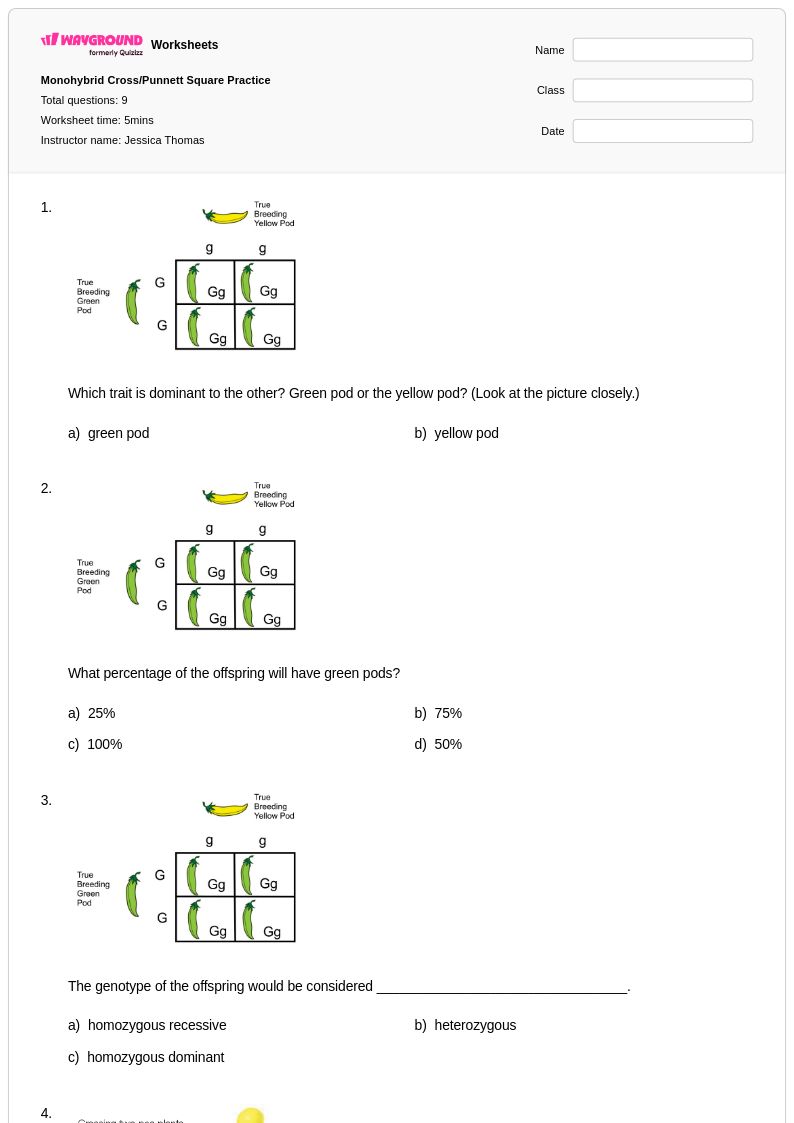
9 Q
9th - 12th

10 Q
10th

25 Q
10th - Uni

30 Q
10th

8 Q
8th
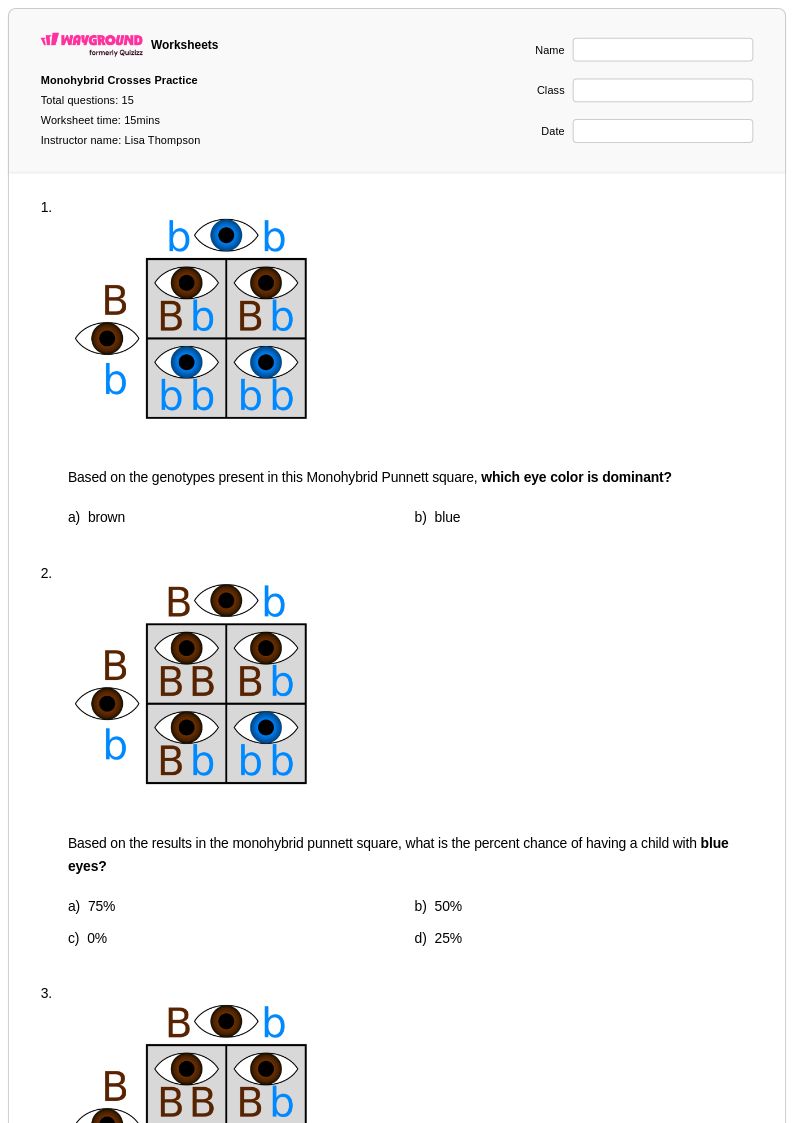
15 Q
10th - Uni

12 Q
10th - 12th

21 Q
9th

20 Q
11th

9 Q
9th

15 Q
9th - Uni
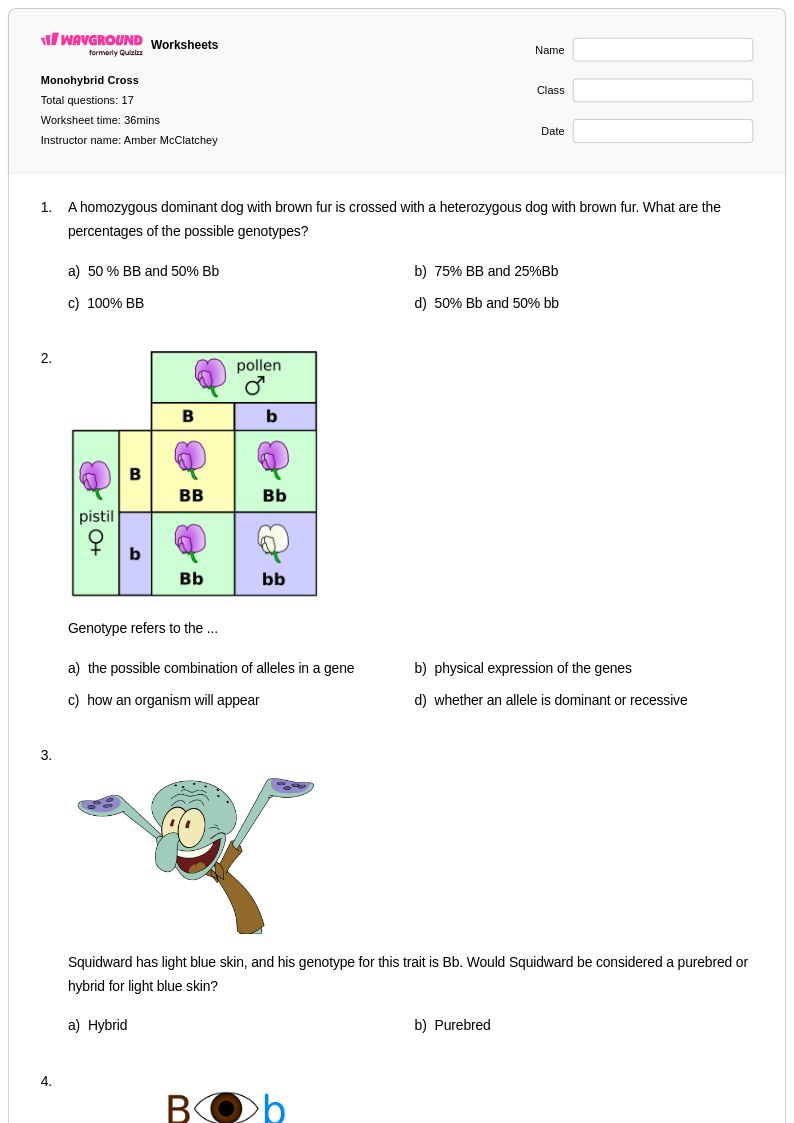
17 Q
9th

7 Q
10th

15 Q
10th - Uni

15 Q
10th - Uni

25 Q
9th
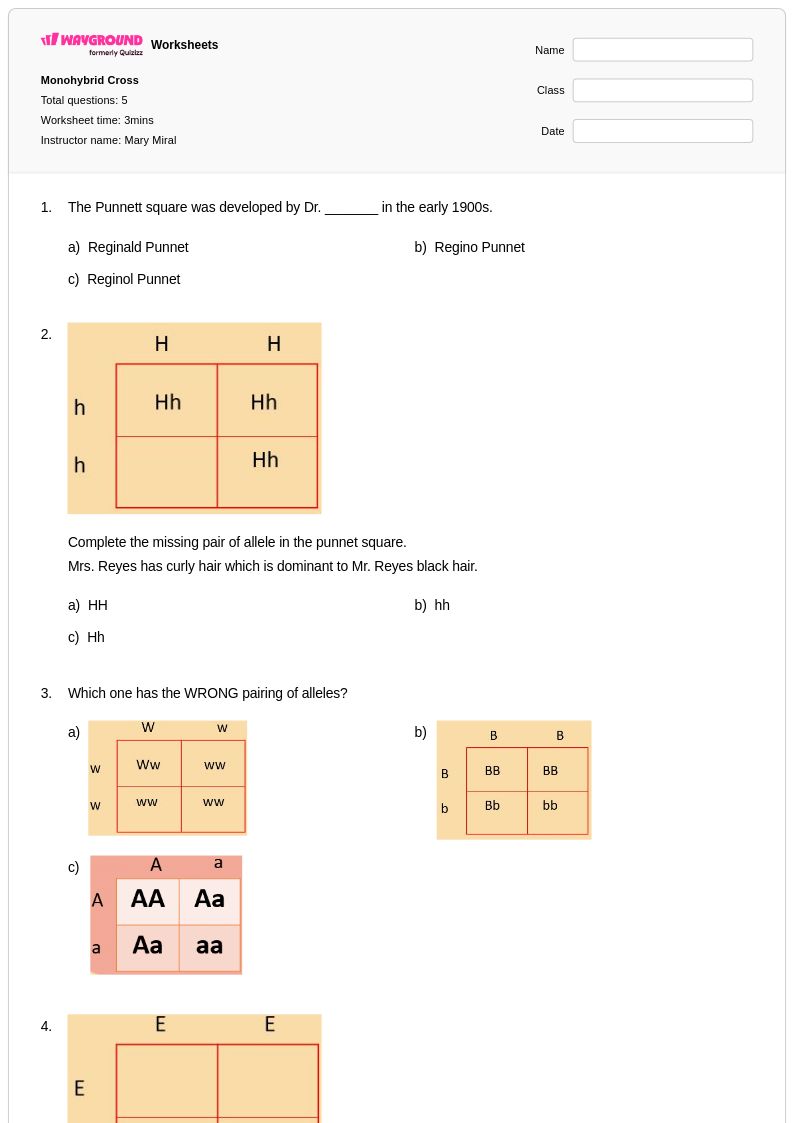
5 Q
8th

5 Q
8th

10 Q
9th - 10th
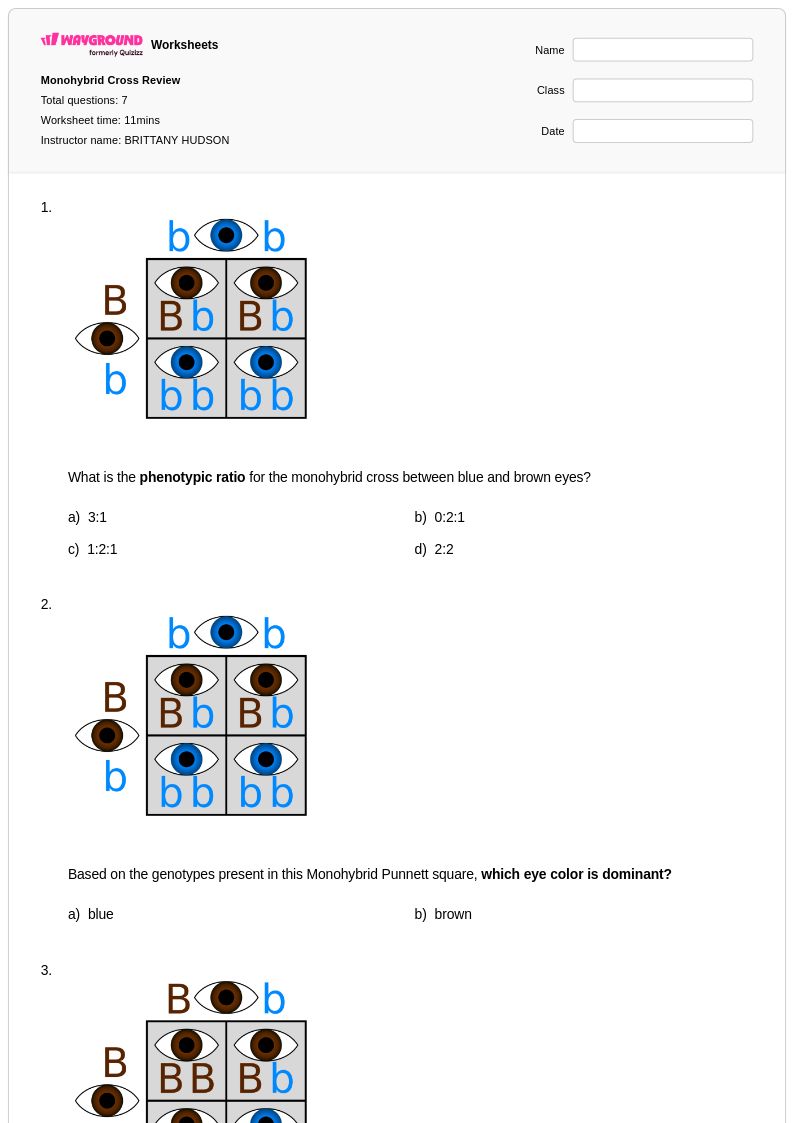
7 Q
9th
Explore Worksheets by Subjects
Explore printable Monohybrid Cross worksheets
Monohybrid cross worksheets available through Wayground (formerly Quizizz) provide students with comprehensive practice in understanding single-trait inheritance patterns and Punnett square construction. These educational resources strengthen critical genetics skills including genotype and phenotype identification, probability calculations, and the application of Mendel's laws of inheritance. Students work through systematic practice problems that reinforce concepts of dominant and recessive alleles, homozygous and heterozygous crosses, and phenotypic ratios. The collection includes printables with detailed answer keys, free downloadable pdf formats, and varied difficulty levels that help students master the fundamental principles of genetic crosses through hands-on problem-solving exercises.
Wayground (formerly Quizizz) supports science educators with millions of teacher-created monohybrid cross resources that streamline genetics instruction and assessment preparation. The platform's robust search and filtering capabilities allow teachers to quickly locate worksheets aligned with specific curriculum standards and learning objectives. Advanced differentiation tools enable customization of content complexity, while flexible formatting options provide both printable pdf versions and interactive digital alternatives to accommodate diverse classroom needs. These comprehensive worksheet collections facilitate targeted skill practice, support remediation for struggling students, offer enrichment opportunities for advanced learners, and help teachers efficiently plan engaging genetics lessons that build student confidence in analyzing inheritance patterns and solving genetic probability problems.
